Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe, how you will proceed to determine the position of the pole of a bar magnet.
Solution
Fix a white sheet of paper on a wooden drawing board and in the middle of it draw a straight line. On the straight line place a magnetic needle. Turn the drawing board in the clockwise or anticlockwise direction, till the magnetic needle is in line with
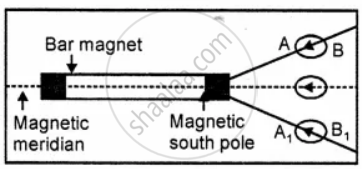
line drawn on drawing board. At this point drawing board is in magnetic meridian. Remove the magnetic needle.
Place a bar magnet such that its axis coincides with this line. Mark the outline of the magnet with a pencil. Place the compass needle near one end of the bar magnet. In this position, the action of the earth’s field is ineffective in deflecting the needle and the compass needle is acted on by the nearest pole only. Market the two ends of the needle by two dots A and B as shown in the figure.
Change the position of the compass needle and repeat the process. Join the two marks A, B, and A,, B, by straight lines. It will be found that the straight lines, when produced, intersect at a point near the end of the magnet. This point of intersection indicates the position of the magnetic pole. Similarly, the other pole may be ascertained in the same way as described above. The length between the two poles is called the effective length of the magnet which is found to be about 0.84 times the actual length of the magnet.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write true or false of the following statement.
Copper cannot be magnetised.
Answer the following.
Can you bring two similar poles of two different magnetic close together easily? Why?
If a bar magnet is cut into equal pieces by cutting it at right angles to its axis at two places, ______ bar magnets are formed, and a total of _____ poles are formed.
There is repulsion between the _____ poles of a magnet and attraction between its _____ poles.
Describe two simple experiments to support the statement that magnetism is a property of the molecules of a magnet.
Bar magnets are often stored in pairs as shown in the figure. E and F being pieces of metal.

Mark on the diagram the poles of the second magnet,
If a magnet is carefully broken into two pieces as shown in figure (i), how does the magnetic strength of each piece compare with that of the original magnet? If another magnet is carefully broken in half along its long axis shown in figure (ii), how would the strength of each piece compare with that of the original magnet?
State three important properties of a magnet.
Write a short note on lighting conductors.
Define natural magnet.
