Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe the construction of Daniel cell. Write the cell reaction.
Solution
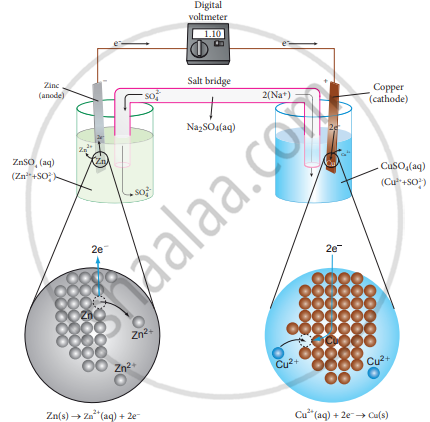
The separation of half reaction is the basis for the construction of Daniel cell. It consists of two half cells.
Oxidation half cell:
The metallic zinc strip dips into an aqueous solution of zinc sulphate taken in a beaker.
Reduction half cell:
A copper strip that dips into an aqueous solution of copper sulphate is taken in a beaker.
Joining the half cell:
The zinc and copper strips are externally connected using a wire through a switch (k) and a load (example: volt meter). The electrolytic solution present in the cathodic and anodic compartment are connected using an inverted U tube containing a agar-agar gel mixed with an inert electrolyte such as KCl, Na2SO4, etc.,
The ions of inert electrolyte do not react with other ions present in the half cells and they are not either oxidised (or) reduced at the electrodes. The solution in the salt bridge cannot get poured out, but through which the ions can move into (or) out of the half cells.
When the switch (k) closes the circuit, the electrons flow from the zinc strip to the copper strip. This is due to the following redox reactions which are taking place at the respective electrodes.
Daniel cell
Anodic oxidation:
The electrode at which the oxidation occurs is called the anode. In Daniel cell, the oxidation take place at zinc electrode, i.e., zinc is oxidised to Zn2 ions and electrons. The Zn2 ions enter the solution and the electrons enter the zinc metal, then flow through the external wire and then enter the copper strip. Electrons are liberated at zinc electrode and hence it is negative (–ve).
\[\ce{Zn_{(s)} -> Zn^{2+}_{( aq)} + 2e^-}\] (loss of electron-oxidation)
Cathodic reduction:
As discussed earlier, the electrons flow through the circuit from zinc to copper, where the Cu2+ ions in the solution accept the electrons, get reduced to copper and the same get deposited on the electrode. Here, the electrons are consumed and hence it is positive (+ve).
\[\ce{Cu^{2+}_{( aq)} + 2e^- -> Cu_{(s)}}\] (gain of electron-reduction)
Salt bridge:
The electrolytes present in two half cells are connected using a salt bridge. We have learnt that the anodic oxidation of zinc electrodes results in an increase in the concentration of Zn2+ in the solution. i.e., the solution contains more number of Zn2+ ions as compared to \[\ce{SO^{2-}_4}\] and hence the solution in the anodic compartment would become positively charged.
Similarly, the solution in the cathodic compartment would become negatively charged as the Cu2+ ions are reduced to copper i.e., the cathodic solution contains more \[\ce{SO^{2-}_4}\] ions compared to Cu2+.
Completion of circuit:
Electrons flow from the negatively charged zinc anode into the positively charged copper electrode through the external wire, at the same time, anions move towards the anode and cations are move towards the cathode compartment. This completes the
circuit.
Consumption of Electrodes:
As the Daniel cell operates, the mass of the zinc electrode gradually decreases while the mass of the copper electrode increases and hence the cell will function until the entire metallic zinc electrode is converted into Zn2+ the entire Cu2+ ions are converted into metallic copper.
Galvanic cell notation:
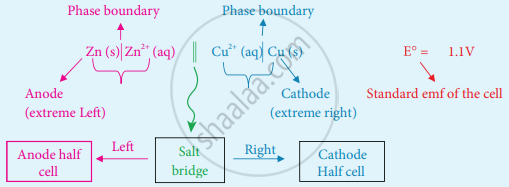
The galvanic cell is represented by a cell diagram, for example, Daniel cell is represented as
\[\ce{Zn_{(s)}|Zn^{2+}_{( aq)}||Cu^{2+}_{( aq)}||Cu_{(s)}}\]
In the above notation, a single vertical bar (|) represents a phase boundary and the double vertical bar (||) represents the salt bridge.
The anode half cell is written on the left side of the salt bridge and the cathode half cell is on the right side.
The anode and cathode are written on the extreme left and extreme right, respectively.
The emf of the cell is written on the right side after the cell diagram.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Derive a relation between ΔH and ΔU for a chemical reaction. Draw neat labelled diagram of calomel electrode. Resistance and conductivity of a cell containing 0.001 M KCI solution at 298K are 1500Ω and 1.46x10-4 S.cm-1 respectively.
A solution of Cu(NO3)2 is electrolyzed between platinum electrodes using 0.1 Faraday electricity. How many moles of Cu will be deposited at the cathode?
Why is anode in galvanic cell considered to be negative and cathode positive electrode?
Write a note on sacrificial protection.
The electrochemical cell stops working after some time because
If the half-cell reaction A + e– → A– has a large negative reduction potential, it follow that:-
On which electrode the oxidation reaction takes place?
In a solution of CuSO4, how much time will be required to precipitate 2 g copper by 0.5 ampere current?
Can we construct an electrochemical cell with two half-cells composed of ZnSO4 solution and zinc electrodes? Explain your answer.
Explain the types of electrochemical cells.
