Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe the function of a transistor as an amplifier with the neat circuit diagram. Sketch the input and output wave forms.
Solution
i. Amplification is the process of increasing the signal strength (increase in the amplitude)
ii. NPN transistor is connected in CE configuration
iii. To start with, the Q point is fixed to get a maximum signal swing at the output.
iv. RC – to measure the output voltage
C1 allows only AC signals to pass,
Bypass capacitor CE provides a low resistance path
Coupling capacitor CC is used to couples the next stage amplifier.
Vs input source signal
IC = BIB `(∴ "B" = "I"_"C"/"I"_"B")`
VCE = VCC – ICRC
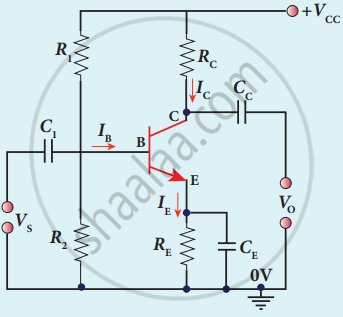
Transistor as an amplifier

Input and output waveforms showing 180° phase reversal.
Working of the amplifier:
a. Working of the amplifier:
- Input signal Vs increases the forward voltage across the emitter-base. IB increases. also increases IC also increases β times.
- This increases the voltage drop across Rc which decreases VCE.
- Therefore input signal in the positive direction produces an amplified signal in the negative direction at the output. Hence output signal is reversed by 180°.
b. During negative half cycle:
- Input signal Vs decreases the forwarded voltage across the emitter-base. As a result, IB decreases IC increases.
- Increase in IC decreases potential drop across Rc and increases VCE.
- Input signal in negative direction produces an amplified signal in the positive direction at the output.
- Therefore 180° phase reversal is observed during the negative half signal.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
In a common-base connection, a certain transistor has an emitter current of 10mA and a collector current of 9.8 mA. Calculate the value of the base current.
The light emitted in an LED is due to
Explain the current flow in an NPN transistor.
Sketch the static characteristics of a common emitter transistor and bring out the essential features of input and output characteristics.
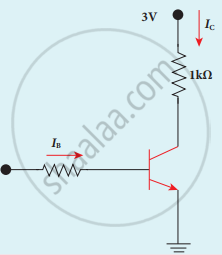
Assuming VCEsat = 0.2 V and β = 50, find the minimum base current (IB) required to drive the transistor given in the figure to saturation.
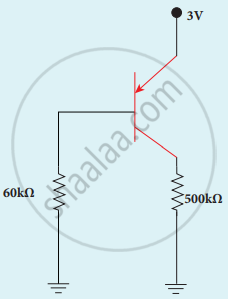
In the circuit shown in the figure, the BJT has a current gain (β) of 50. For an emitter-base voltage VEB = 600 mV, calculate the emitter-collector voltage VEC (in volts).
A transistor having α = 0.8 is connected in common emitter configuration. When the base current changes by 6 mA, then the change in collector current is ______.
ln switching circuit, transistor is in ON state and values of IC and IB are 4.2 mA and 5 µA respectively and RC= l k`Omega` and RB= 300 k`Omega`. If VBE = 0.5 V, find the value of VBB.
A pnp transistor is used in common-emitter mode. If a change of 40 µA in base current brings a change of 2 µA in collector current with 0.04 V in base-emitter voltage, then the input resistance is ____________.
In a transistor, doping level in base is increased slightly, the collector current and base current respectively ______.
