Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Describe the structure of diborane.
Solution
In diborane, two BH2 units are linked by two bridged hydrogens. Therefore, it has eight B-H bonds. However, diborane has only 12 valance electrons and are not sufficient to form normal covalent bonds. The four-terminal B-H bonds are normal covalent bonds (two centre – two-electron bond or 2c-2e bond). The remaining four electrons have to used for the bridged bonds, i.e. two-three centred B-H-B bonds utilise two electrons each.
Hence, these bonds are three centre – two-electron bonds. The bridging hydrogen atoms are in a plane as shown in the figure. In dibome, the boron is sp3 hybridised. Three of the four sp3 hybridised orbitals contains a single electron and the fourth orbital is empty.
Two of the half-filled hybridised orbitals of each boron overlap with the two hydrogens to form four-terminal 2c-2e bonds, leaving one empty and one half filled hybridised orbitals on each boron. The Three centre – two-electron bonds, B-H-B bond formation involves overlapping the half-filled hybridised orbital of one boron, the empty hybridised orbital of the other boron and the half-filled 1s orbital of hydrogen.
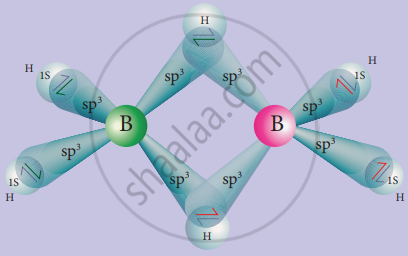
Structure of diborane
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An aqueous solution of borax is ____________.
Match items in Column – I with the items of Column – II and assign the correct code.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| A. Borazole | 1. B(OH)3 |
| B. Boric acid | 2. B3N3H6 |
| C. Quartz | 3. Na2[B4O5(OH)4]8H2O |
| D. Borax | 4. SiO2 |
Duralumin is an alloy of ____________.
Give the uses of Borax.
Give one example for the following.
Icosogens
Complete the following reaction.
\[\ce{B(OH)3 + NH3 ->}\]
Complete the following reaction.
\[\ce{B2H6 +CH3OH ->}\]
Complete the following reaction.
\[\ce{BF3 + 9H2O ->}\]
How will you convert boric acid to boron nitride?
A hydride of 2nd period alkali metal (A) on reaction with a compound of Boron (B) to give a reducing agent (C). identify A, B and C.
