Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Determine the current flowing through the galvanometer (G) as shown in the figure.
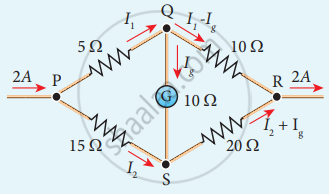
Solution
I2 = I – I1
Current flowing through the circuit I = 2A
Applying Kirchhoffs II law to PQSP
5I1 + 10Ig – 15I2 = 0
5I1 + 10Ig – 15(I – I1) = 0
5I1 + 10Ig – 15I + 15I1 = 0
20I1 + 10Ig = 15 × I
20I1 + 10Ig = 30
2I1 + Ig = 3 ………..(1)
Applying Kirchhoffs II law to QRSQ
10(I1 – Ig) – 20 (I2 + Ig) – 10 Ig = 0
10I1 – 10 Ig – 20 (I – I1 + Ig) – 10 Ig = 0
10I1 – 10 Ig – 20I + 20I1 – 20Ig – 10Ig = 0
30I1 – 40Ig = 20I
30I1 – 40Ig = 20 × 2
3I1 – 4Ig = 4 ………..(2)
(1) × 3 ⇒ 6I1 + 3Ig = 9 …………..(3)
(2) × 2 ⇒ 6I1 – 8Ig = 8 ……………(4)
Solving (3) and (4)
+ 11 Ig = 1
Ig = `1/11`A
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The internal resistance of a 2.1 V cell which gives a current of 0.2 A through a resistance of 10Ω is ______.
What do you mean by internal resistance of a cell?
Explain the determination of the internal resistance of a cell using voltmeter.
Three identical lamps each having a resistance R are connected to the battery of emf as shown in the figure.
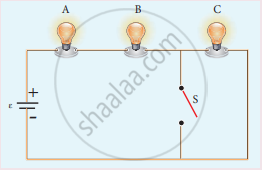
Suddenly the switch S is closed.
- Calculate the current in the circuit when S is open and closed.
- What happens to the intensities of the bulbs A, B and C.
- Calculate the voltage across the three bulbs when S is open and closed.
- Calculate the power delivered to the circuit when S is opened and closed.
- Does the power delivered to the circuit decrease, increase or remain same?
A cell supplies a current of 0.9 A through a 2 Ω resistor and a current of 0.3 A through a 7 Ω resistor. Calculate the internal resistance of the cell.
