Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Differentiate between Conductors and insulators.
Solution
| Conductors | Insulators |
|
Those substances through which electricity can flow are called conductors. |
Those substances through which electricity cannot flow are called insulators. |
| Electrical resistances of conductors are very low. | Electrical resistances of insulators are infinitely very high. |
|
They contain a large number of free electrons. |
They do not contain free electrons. |
|
Generally, metals are conductors. E.g. silver, copper, aluminium |
Generally non – metals are insulators. E.g. wood, rubber, plastic |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The magnetic field in a given region is uniform. Draw a diagram to represent it.
Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer.)
Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer.)
Name the rule for finding the direction of magnetic field produced by a straight current-carrying conductor.
State the form of magnetic field lines around a straight current-carrying conductor.
What is the shape of a current-carrying conductor whose magnetic field pattern resembles that of a bar magnet?
What are the various ways in which the strength of magnetic field produced by a current-carrying circular coil can be increased?
Name the type of magnet with which the magnetic field pattern of a current-carrying solenoid resembles
What type of core should be put inside a current-carrying solenoid to make an electromagnet?
A soft iron bar is inserted inside a current-carrying solenoid. The magnetic field inside the solenoid:
(a) will decrease
(b) will increase
(c) will become zero
(d) will remain the same
What happens when a current-carrying conductor is placed in a magnetic field?
State two ways to increase the force on a current-carrying conductor in a magnetic field.
A current flows in a wire running between the S and N poles of a magnet lying horizontally as shown in Figure below:
The force on the wire due to the magnet is directed:

fron N to S
from S to N
vertically downwards
vertically upwards
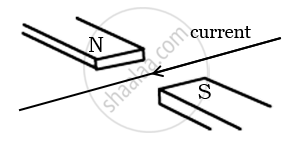
A horizontal wire carries a current as shown in Figure below between magnetic poles N and S:

Is the direction of the force on the wire due to the magnet:
(a) in the direction the current
(b) vertically downwards
(c) opposite to the current direction
(d) vertically upwards
If the current in a wire is flowing in the vertically downward direction and a magnetic field is applied from west to east, what is the direction of force in the wire?
force experienced by a current-carrying straight conductor placed in a magnetic field which is perpendicular to it.
Name and state the law which is used to determine the direction of force on a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field.
How will the direction of force be changed, if the current is reversed in the conductor placed in a magnetic field?
State the unit of magnetic field in terms of the force experienced by a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field
A coil ABCD mounted on an axle is placed between the poles N and S of a permanent magnet as shown in Figure.
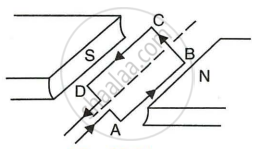
- In which direction will the coil begin to rotate when current is passed through the coil in direction ABCD by connecting a battery at the ends A and D of the coil?
- Why is a commutator necessary for continuous rotation of the coil?
- Complete the diagram with commutator, etc. for the flow of current in the coil?
State whether a magnetic field is associated or not around a static charge.
State under what conditions force acting on a current carrying conductor which is freely suspended in a magnetic field can be maximum.
Write Fleming’s left hand rule.
The shape of the magnetic field lines produced by a current-carrying conductor is ____________.
A current flows in a wire running between the S and N poles of a magnet lying horizontally as shown in the figure below:
The force on the wire due to the magnet is directed ____________.
The strength of magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor is ____________.
When current is parallel to a magnetic field, then force experience by the current-carrying conductor placed in a uniform magnetic field is ____________.
A magnetic field directed in north direction acts on an electron moving in east direction. The magnetic force on the electron will act ____________.
The direction of force on a current carrying conductor in a magnetic field is given by ____________.
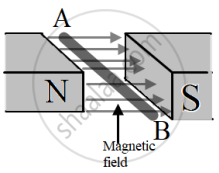
The diagram below shows a free conductor AB is kept in a magnetic field and is carrying current from A to B. (To avoid confusion complete path of the circuit is not shown) The direction of the force experienced by the conductor will be:
What do you know about Michael Faraday?
Observe the given figure of Fleming's Left Hand Rule and write the labels of 'A' and 'B':

Which of the following pattern correctly describes the magnetic field around a long straight wire carrying current?
|
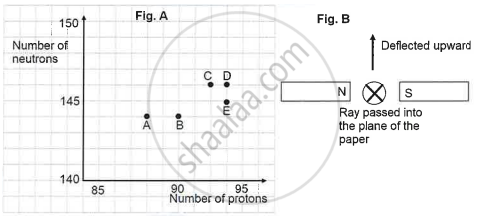
The graph (fig A) illustrates the correlation between the number of protons (x-axis) and the number of neutrons (y-axis) for elements A, B, C, D, and E in the periodic table. These elements are denoted by the letters rather than their conventional symbols. When the element C, depicted in the graph, undergoes radioactive decay, it releases radioactive rays. When these rays are directed into the plane of the paper in the presence of a magnetic field, as indicated in the fig B, they experience deflection, causing them to move upwards.
|
Name the law used to identify the radioactive radiation emitted by the element.