Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
Differentiate between Conductors and insulators.
उत्तर
| Conductors | Insulators |
|
Those substances through which electricity can flow are called conductors. |
Those substances through which electricity cannot flow are called insulators. |
| Electrical resistances of conductors are very low. | Electrical resistances of insulators are infinitely very high. |
|
They contain a large number of free electrons. |
They do not contain free electrons. |
|
Generally, metals are conductors. E.g. silver, copper, aluminium |
Generally non – metals are insulators. E.g. wood, rubber, plastic |
APPEARS IN
संबंधित प्रश्न
The magnetic field in a given region is uniform. Draw a diagram to represent it.
The magnetic field inside a long straight solenoid-carrying current ______.
Which of the following property of a proton can change while it moves freely in a magnetic field? (There may be more than one correct answer.)
A positively-charged particle (alpha-particle) projected towards west is deflected towards north by a magnetic field. The direction of magnetic field is ______.
State Fleming’s left-hand rule.
Which of the following correctly describes the magnetic field near a long straight wire?
State whether the following statement is true or false
The field at the centre of a long circular coil carrying current will be parallel straight lines.
When is the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
What concealed do you get from the observation that a current-carrying wire deflects a compass needle placed near it?
State whether the following statement is true or false:
The magnetic field inside a long circular coil carrying current well be parallel straight lines.
Name and state the rule to determine the direction of magnetic field around a straight current-carrying conductor.
Name any two factors on which the strength of magnetic field produced by a current-carrying solenoid depends. How does it depend on these factors?
List three ways in which the magnetic field strength of a current-carrying solenoid can be increased?
The diagram given below represents magnetic field caused by a current-carrying conductor which is:
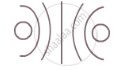
(a) a long straight wire
(b) a circular coil
(c) a solenoid
(d) a short straight wire
When is the force experienced by a current-carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field largest?
For Fleming's left-hand rule, write down the three things that are 90° to each other, and next to each one write down the finger or thumb that represents it.
The force exerted on a current-carrying wire placed in a magnetic field is zero when the angle between the wire and the direction of magnetic field is:
45°
60°
90°
180°
If the current in a wire is flowing in the vertically downward direction and a magnetic field is applied from west to east, what is the direction of force in the wire?
Which way does the wire in the diagram below tend to move?
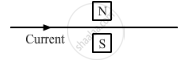
What is the force on a current-carrying wire that is parallel to a magnetic field? Give reason for your answer.
Two coils A and B of insulated wire are kept close to each other. Coil A is connected to a galvanometer while coil B is connected to a battery through a key. What would happen if:
the current is stopped by removing the plug from the key?
Explain your answer mentioning the name of the phenomenon involved.
State the unit of magnetic field in terms of the force experienced by a current carrying conductor placed in a magnetic field
Name and state the rule of determine the direction of force experienced by a current carrying straight conductor placed in a uniform magnetic field which is perpendicular to it.
A flat coil ABCD is freely suspended between the pole of a U-shaped permanent magnet with the plane of coil parallel to the magnetic field.
Name an instrument which makes use of the principle stated above.
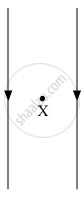
The following diagram shows two parallel straight conductors carrying the same current. Copy the diagram and draw the pattern of the magnetic field lines around them showing their directions. What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at a point 'X' which is equidistant from the conductors? Give justification for your answer.
Write Fleming’s left hand rule.
The north pole of Earth’s magnet is in the ____________.
A current-carrying conductor is held in an exactly vertical direction. In order to produce a clockwise magnetic field around the conductor, the current should be passed in the conductor:
The shape of the magnetic field lines produced by a current-carrying conductor is ____________.
The strength of magnetic field around a current-carrying conductor is ____________.
When current is parallel to a magnetic field, then force experience by the current-carrying conductor placed in a uniform magnetic field is ____________.
For a current in a long straight solenoid N- and S-poles are created at the two ends. Among the following statements, the incorrect statement is
What do you know about Michael Faraday?
Assertion (A): A magnetic field exerts a force on a moving charge in the same direction as the direction of the field itself.
Reason (R): The direction of force is given by Fleming’s left-hand rule.
A current-carrying conductor of a certain length, kept perpendicular to the magnetic field experiences a force F. What will be the force if the current is increased four times, the length is halved and the magnetic field is tripled?
A copper wire is held between the poles of a magnet
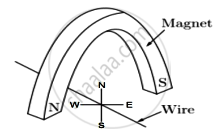
The current in the wire can be reversed. The pole of the magnet can also be changed over. In how many of the four directions shown can the force act on the wire?
Which of the following pattern correctly describes the magnetic field around a long straight wire carrying current?
