Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Differentiate between Myelinated and non-myelinated axons.
Solution
| Myelinated axons | non-myelinated axons | |
| 1. | Nerve impulse conduction is saltatory. | Nerve impulse conduction is smooth. |
| 2. | Myelinated axon have a myelin sheath. | Myelin sheath is absent. |
| 3. | Node of Ranvier is present between adjacent myelin sheaths. | Node of Ranvier is absent. |
| 4. | Found in the brain, the spinal cord, the cranial and spinal nerves | Found in autonomous and somatic neural systems |
| 5. | Schwann cells are observed inside the myelin sheath | Schwann cells are not observed inside the myelin sheath |
| 6. | Schwann cells in axons generate myelin sheaths. | The myelin sheath is lacking. |
| 7. | Voltage-gated ion channels are concentrated at the nodes, and depolarization only occurs there. | Voltage-gated ion channels are found throughout the axon, and depolarization occurs along the length of the nerve fibre. |
| 8. | Ion exchange can only happen at the nodes. | Ion exchange happens over the surface. |
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Renal cortex and Renal medulla [Parts of the nephrons present]
Differentiate between Spinal nerves and Cranial nerves (number of nerves).
Mention the exact location of Malleus
Describe three kinds of nerves, giving the example of each.
Fill in the blank:
Basic structural unit of the nervous system is the________.
Define the term Motor neuron.
Mention the types of nerves found in humans.
Complete the following statement by choosing the correct alternative from the choice given in below :
The dorsal root ganglion of the spinal cord contains cell bodies of ________ neurons.
Write the function of Association neuron.
Explain the following term :
Association neuron
Write a short note.
Autonomic Nervous System
______ is the longest cell in our body.
A microscopic gap between a pair of adjacent neurons over which nerve impulses pass is called ____________.
Assertion: Impulse travels from dendrite to cell body and then along the axon to its end.
Reason: Information acquired at the end of the dendrite tip of a nerve cell sets of an electric impulse.
Write one word for the following:
wave of electrical disturbance that sweeps over the nerve cell.
Write one word for the following:
The kind of nerve carrying impulses from the brain to a gland or muscle.
Name the following:
Three types of nerves.
The figure given below is the basic structural and functional unit of the human nervous system. Study the diagram and answer the following questions:
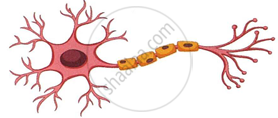 |
- Write the technical term for the diagram.
- Name two organs of our nervous system where these cells are richly found.
- How are these cells significant for us?
- Name the cell organelle that is absent in these cells and how does it affect our body metabolism?
- Redraw the same figure and label the following Perikaryon, Axon, Dendrites, Myelin sheath and Node of Ranvier.
