Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the following:
Mechanism through which a sound produces a nerve impulse in the inner ear.
Solution
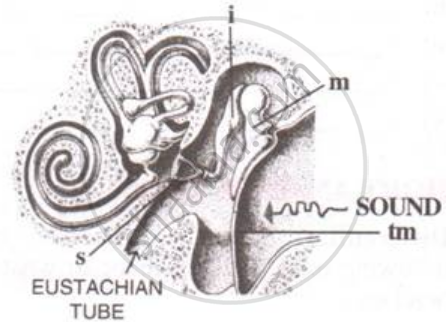
The pinna of the external ear collects the sound waves and directs them to the tympanic membrane (ear drum) via the external auditory canal. The ear drum then vibrates the sound waves and conducts them to the internal ear through the ear ossicles. The ear ossicles increase the intensity of the sound waves. These vibrating sound waves are conducted through the oval window to the fluid in the cochlea. Consequently, a movement is created in the lymph. This movement produces vibrations in the basilar membrane, which in turn stimulate the auditory hair cells. These cells generate a nerve impulse, conducting it to the auditory cortex of the brain via afferent fibres. The auditory cortex region interprets the nerve impulse and sound is recognised.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following:
Which part of the ear determines the pitch of a sound?
The unit of frequency is ______.
Briefly explain the following terms: Power of accommodation
Where is the Semicircular canals located? Briefly mention its function.
Name the part of the ear associated with dynamic balance.
What is the name of passage in outer ear which carries sound waves to the ear-drum ?
Why should we not put a pin or pencil in our ears ?
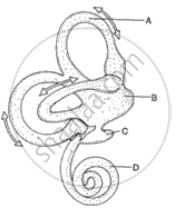
The diagram alongside represents the structure found in the inner ear. Study the same and then answer the questions that follow:
(i) Name the parts labelled A, B, C and D.
(ii) Name the parts of the ear responsible for transmitting impulses to the brain.
(iii) Name the part labelled above which is responsible for:
1. Static equilibrium. 2. Dynamic equilibrium. 3. Hearing
(iv) Name the audio receptor cells which pick up vibrations.
(v) Name the fluid present in the inner ear.
The figure below is the sectional view of a part of the skull showing a sense organ:
What do you call the part shown in the form of a spiral? What is its function?
Differentiate between:
Cochlea and Concha.
The following diagram refers to the ear of a mammal.

(i) Label the parts 1 to 10 to which the guidelines point.
(ii) Which structure:
(a) converts sound waves into mechanical vibrations?
(b) Converts vibrations into nerve impulses?
(c) Responds to change in position?
(d) Transmits impulses to the brain?
(e) Equalizes atmospheric pressure and pressure in the ear.
Given below is the diagram of the human ear. Study the diagram and then answer the questions that follow:

(i) What role does the eardrum play in hearing?
(ii) What common term is given to the parts labeled A, B, and E?
(iii) Would there be any difference if these three parts mentioned in (ii) above were replaced by one by one? Why?
(iv) Give the biological term for the parts labeled C and D.
(v) Name the fluid which fills the parts mentioned in (iv) above.
(vi) State the functions of the ear.
Choose the Odd One Out:
Name the three ossicles of the middle ear.
The part of the ear that turns pressure variations into electrical signals is ______.
In the inner ear, the pressure variations are turned into electrical signals by the ______.
Vibrating particles travel all the way from the vibrating objects to the ear.
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place.
Eyes: Photoreceptors :: Ears : ______.
Note the relationship between the first two words and suggest the suitable word/words for the fourth place.
Ear pinna : Auricle :: Inner ear : ______.
With reference to human ear answer the question that follow:
Name the part of the ear associated with dynamic balance.
