Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a scientifically correct labelled diagram of a human eye and answer the questions based on it:
- Name the type of lens in the human eye.
- Name the screen at which the maximum amount of incident light is refracted?
- State the nature of the image formed of the object on the screen inside the eye.
Solution

- The human eye's lens is a transparent, crystalline double convex lens.
- Maximum amount of incident light is refracted inside the eye at the outer surface of the cornea.
- The image of the object created on the inside screen of the eye is real and inverted.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the function of the following part of the human eye: ciliary muscles
Explain the following:
Mechanism of generation of light-induced impulse in the retina.
Myopia is an example of ______.
Name two types of cells in the retina of an eye which respond to light.
Out of rods and cones m the retina of your eye:
which detect colour?
What changes take place in the shape of eye-lens:
when the eye is focused on a distant object?
Ciliary muscles of human eye can contract or relax. How does it help in the normal functioning of the eye?
There are two types of light-sensitive cells in the human eye:
Where are they found?
There are two types of light-sensitive cells in the human eye:
To what is each type of cell sensitive?
The human eye possesses the power of accommodation. This is the power to:
(a) alter the diameter of the pupil as the intensity of light changes
(b) distinguish between lights of different colours
(c) focus on objects at different distances
(d) decide which of the two objects is closer.
The size of the pupil of the eye is adjusted by:
(a) cornea
(b) ciliary muscles
(c) optic nerve
(d) iris
Which parts of the eye cause rays of light to converge on the retina?
Nocturnal animals (animals which sleep during the day and come out at night) tend to have wide pupils and lot of rods in their retinas. Suggest reasons for this.
Name two animals having eyes:
one the sides of the head.
Mention the characteristics of the image that falls on the retina of the eye.
Name the following:
Short sightedness.
Name the respective organs in which the following are located and mention the main function of each:
(i) Iris
(ii) Semicircular canals
Differentiate between:
Retina and Choroid.
Explain the Term: Accommodation in the eye
Mention, if the following statement is True or False
Rods are responsible for vision in the dark
Complete the following sentence with appropriate Word
The part of the human eye where rod cells and cone cells are located is the:
For a normal human eye the near point is at _______.
Name the capacity of the eye lens to change its focal length as per need.
Write an Explanation.
Power of accommodation
Why the human eye is compared with camera?
In a myopic eye, the image of the object is formed
Assertion: Blind spot is a small area of the retina which is insensitive to light where the optic nerve leaves the eye.
Reason: There are no rods or cones present at the junction of the optic nerve and retina in the eye.
Given below is a diagram depicting a defect of the human eye. Answer the questions that follow:
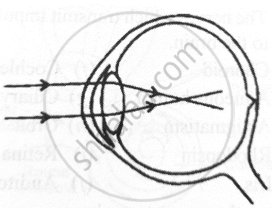
- Give the scientific term for the defect.
- Mention one possible reason for the defect.
- What type of lens can be used to correct the defect?
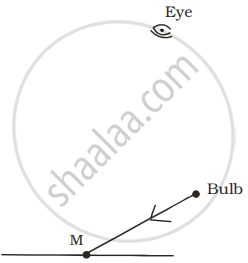
A tiny mirror M is fixed on a piece of cardboard placed on a table. The cardboard is illuminated by light from a bulb. The position of eye with respect to position of bulb is shown in the figure as A, B, C and D. In which position mirror will be visible?
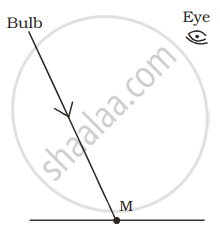 |
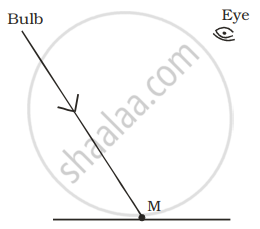 |
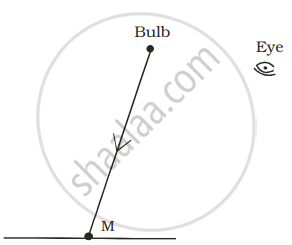 |
 |
| (A) | (B) | (C) | (D) |
Match the following
| 1. | Conjunctiva | a. | Coloured part of eye |
| 2. | Cornea | b. | Photosensitive layer |
| 3. | Iris | c. | Refraction |
| 4. | Retina | d. | Protection |
In human eye the part which allows light to enter into the eye is ______.
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a) Path way of light |
| 2. Pupil | b) Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c) near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d) Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | e) Power of accommodation |
With neat, labeled diagram describe the structure of retina of eye.
Match the following:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| 1. Retina | a. Path way of light |
| 2. Pupil | b. Far point comes closer |
| 3. Ciliary muscles | c. near point moves away |
| 4. Myopia | d. Screen of the eye |
| 5. Hypermetropia | e. Power of accommodation |
Chris was watching the display of fireworks in the sky.

- Trace the path of the light rays using the following terms:
Fovea, Lens, Conjunctiva, Pupil, Cornea. - Name the nerve that carries the impulse for vision to the brain.
State the functions of the following:
Iris
Which of the following is responsible for the adjustment of the size of pupil?
Write the main functional activity of the following structure.
Choroid
The figure given below refers to the vertical section of the eye of a mammal. Study the figure carefully and answer the following questions.
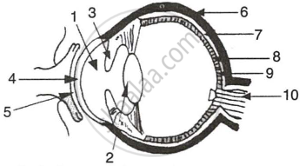 |
- Label the guidelines shown as 1 to 10.
- Write one important role of parts shown as 3 and 7.
- Write one structural difference between the parts shown as 9 and 10.
- Mention one functional difference between the parts shown as 6 and 8.
