Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw a diagram to show how a converging lens focusses parallel rays of light?
Solution
When rays of light from a distant object pass through a converging lens, the light rays converge at the focus of lens (fig.).

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
If the image formed by a lens for all positions of an object placed in front of it is always erect and diminished, what is the nature of this lens? Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer.
Where must the object be placed for the image formed by a converging lens to be:
real, inverted and larger than the object?
Copy and complete the diagram below to show what happens to the rays of light when they pass through the concave lens:
Construct ray diagrams to illustrate the formation of a virtual image using a diverging lens.
A concave lens forms a magnified or diminished image depending on the distance of an object from it.
The diagrams showing the correct path of the ray after passing through the lens are:
 |
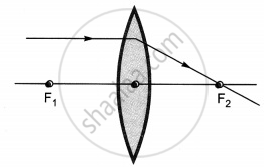 |
| I | II |
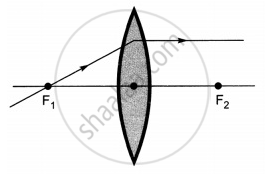 |
 |
| III | IV |
Distinguish between concave and convex lens.
An object is placed at a distance of 60 cm from a concave lens of focal length 30 cm.
(i) Use the lens formula to find the distance of the image from the lens.
(ii) List four characteristics of the image (nature, position, size, erect/inverted) formed by the lens in this case.
(iii) Draw a ray diagram to justify your answer of the part (ii).
Do we expect any change in the position, nature, and size of the image
(i) formed by a concave lens,
(ii) with a change in the position of the object?
Define the principal focus of a concave lens.
