Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
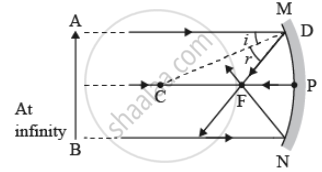
Draw ray diagrams showing the image formation by a concave mirror when an object is placed
- between pole and focus of the mirror
- between focus and centre of curvature of the mirror
- at centre of curvature of the mirror
- a little beyond centre of curvature of the mirror
- at infinity
Solution
The ray diagrams showing the image formation by a concave mirror when an object is placed,
- between pole and focus of the mirror,
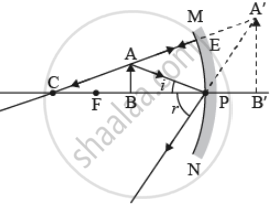
- between focus and centre of curvature of the mirror,
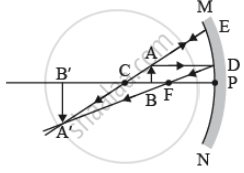
- at centre of curvature of the mirror,
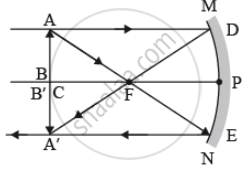
- a little beyond centre of curvature of the mirror,
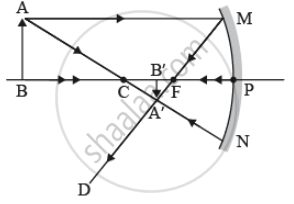
- at infinity,
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw ray diagrams for the cases of images obtained in concave mirrors as described in the table below.
| Images formed by concave mirrors | ||||
| No. | Position of the object | Position of the image | Nature of image | Size of the image |
| 1 | Between pole and focus | Behind the mirror | Erect, virtual | Magnified |
| 2 | At the focus | At infinity | Inverted, real | Very large |
| 3 | Between focus and centre of curvature | Beyond the centre of curvature | Inverted, real | Magnified |
| 4 | At the centre of curvature |
At the centre of curvature | Inverted, real | Same as the object |
| 5 | Object between infinity and Centre of curvature | Between the centre of curvature and focus | Inverted, real | Diminished |
| 6 | Object at infinity | At focus | Inverted, real | Diminished |
Assertion: For observing the traffic at a hairpin bend in mountain paths a plane mirror is preferred over convex mirror and concave mirror.
Reason: A convex mirror has a much larger field of view than a plane mirror or a concave mirror.
If an object is placed at the focus of a concave mirror, where is the image formed?
- Complete the diagram to show how a concave mirror forms the image of the object.
- What is the nature of the image?
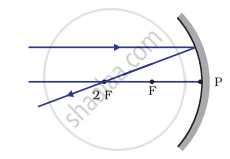
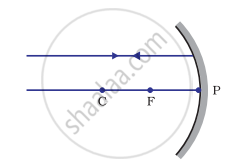
Which of the following ray diagrams is correct for the ray of light incident on a concave mirror as shown in Figure?
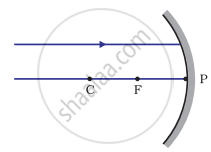
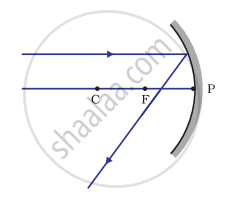 |
 |
 |
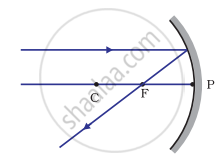 |
| Fig. A | Fig. B | Fig. C | Fig. D |
List four properties of the image formed by the concave mirror when the object is placed between F & P.
Rohit wants to have an erect image of an object using a converging mirror of focal length 40 cm.
- Specify the range of distance where the object can be placed in front of the mirror. Justify.
- Draw a ray diagram to show image formation in this case.
- State one use of the mirror based on the above kind of image formation.
A 10 cm long pencil is placed 5 cm in front of a concave mirror having a radius of curvature of 40 cm.
- Determine the position of the image formed by this mirror.
- What is the size of the image?
- Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image as mentioned in part (i).
