Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Draw ray diagrams showing the image formation by a convex lens when an object is placed
- between optical centre and focus of the lens
- between focus and twice the focal length of the lens
- at twice the focal length of the lens
- at infinity
- at the focus of the lens
Solution
The ray diagrams showing the image formation by a convex lens when an object is placed,
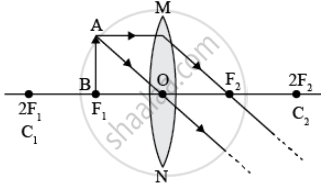
- between optical centre and focus of the lens,
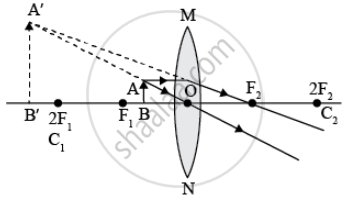
- between focus and twice the focal length of the lens,

- at twice the focal length of the lens,
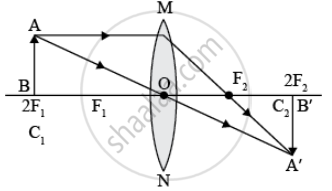
- at infinity,
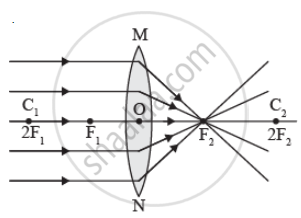
- at the focus of the lens,
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A lens forms an erect, magnified, and virtual image of an object. Draw a labelled ray diagram to show the image formation.
A converging lens forms the image of an object placed in front of it beyond 2F2 of the lens. Where is the object placed?
Draw a ray diagram to show how a converging lens can form an image of the sun. Hence give a reason for the term ‘burning glass’ for a converging lens used in this manner.
For the object placed between the optical centre and focus of a convex lens, the image is ______.
Where should an object be placed so that a real and inverted image of the same size is obtained by a convex lens?
Which of the following lens would you prefer to use while reading small letters found in a dictionary?
Explain the rules for obtaining images formed by a convex lens with the help of ray diagram.
Sudha finds out that the sharp image of the window pane of her science laboratory is formed at a distance of 15 cm from the lens. She now tries to focus the building visible to her outside the window instead of the window pane without disturbing the lens. In which direction will she move the screen to obtain a sharp image of the building? What is the approximate focal length of this lens?
A student focussed the image of a candle flame on a white screen using a convex lens. He noted down the position of the candle screen and the lens as under
Position of candle = 12.0 cm
Position of convex lens = 50.0 cm
Position of the screen = 88.0 cm
- What is the focal length of the convex lens?
- Where will the image be formed if he shifts the candle towards the lens at a position of 31.0 cm?
- What will be the nature of the image formed if he further shifts the candle towards the lens?
- Draw a ray diagram to show the formation of the image in case (iii) as said above.
Complete the following table based on image formation by convex lens:
| Position of Object | Position of Image | Nature of Image |
| At infinity | (a) ______ | Real and inverted and highly diminished image |
| Beyond 2F1 | (b) ______ | (c) ______ |
| At 2F1 | (d) ______ | Real, inverted, same size (as object) image |
| Between F1 and 2F1 | Beyond 2F2 | (e) ______ |
| At focus F1 | (f) ______ | Real, inverted and highly enlarged image |
