Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
During inspiration, the diaphragm ______.
Options
expands
unchanged
relaxes to become domed–shaped.
contracts and flattens
Solution
During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and flattens.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Differentiate between cyclic and non-cyclic photophosphorylation.
Distinguish between photosynthesis and aerobic respiration.
Why do we often sneeze when we inhale a lot of dust-laden air?
During exhalation, the ribs ______.
Write true or false for the following statement. Rewrite the false statement correctly.
Respiration and breathing are two different processes.
In human respiration, chemical energy is released in the form of ______.
Distinguish between inspiration and expiration.
Differentiate between inhalation and exhalation.
For which of the following reasons stepwise cellular respiration is useful?
Which of the following is CORRECT with reference to oxygen dissociation curve?
____________ in mammals do not help in respiration.
The impulse for voluntary muscles for forced breathing starts in ____________.
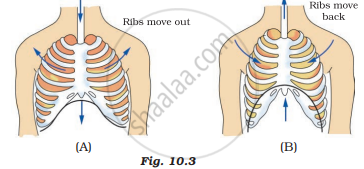
Observe the figures given in Figures 10.3 (A) and (B) and answer the following.
Which of the figures A or B indicates the process of inhalation and which is the process of exhalation?
Lungs do not collapse between breaths and some air always remains in the lungs which can never be expelled because ______.
The partial pressures (in mm Hg) of oxygen (O2) and carbon dioxide (CO2) at alveoli (the site of diffusion) are ______
Mark the true statement among the following with reference to normal breathing.
Identify the wrong statement with reference to the transport of oxygen.
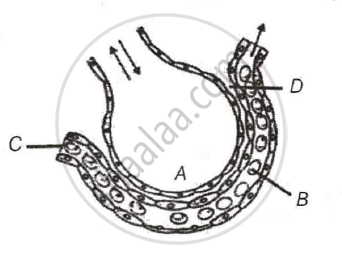
The figure given below shows a small part of human lung where exchange of gas takes place. In which one of the options given below, the one part A, B, C or D is correctly identified along with its function.
What is oxygen dissociation curve?
Complete the table:
| Partial pressure of gases |
Alveolar air | Pulmonary Capillaries |
| PP02 104 | mm Hg | ______ |
| PPC02 40 | mm Hg | ______ |
