Advertisements
Advertisements
प्रश्न
During inspiration, the diaphragm ______.
विकल्प
expands
unchanged
relaxes to become domed–shaped.
contracts and flattens
उत्तर
During inspiration, the diaphragm contracts and flattens.
संबंधित प्रश्न
During exhalation, the ribs ______.
Choose the correct alternative.
_______ muscles contract when the external intercostal muscles contract.
Very short answer question.
Why is a gas exchange very rapid at the alveolar level?
Define total lung capacity.
Define Hamburger’s phenomenon. Add a note on it.
The Tidal Volume of a normal person is ______.
Vital capacity is ______.
After a long deep breath, we do not respire for some seconds due to ______.
Make the correct pairs.
| Column – I | Column – II |
| (P) Tidal volume | i. 1000 to 1100 ml |
| (Q) Residual volume | ii. 500 ml |
| (R) Expiratory reserve volume | iii. 2500 to 3000 ml |
| (S) Inspiratory reserve volume | iv. 1100 to 1200 ml |
CO2 carried from the tissue cells in the blood is in the form of ______.
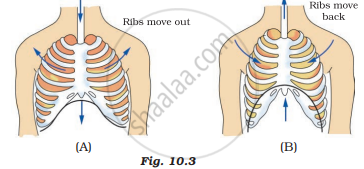
Observe the figures given in Figures 10.3 (A) and (B) and answer the following.
Which of the figures A or B indicates the process of inhalation and which is the process of exhalation?
Mark the true statement among the following with reference to normal breathing.
What is phosphorylation?
Identify the wrong statement with reference to the transport of oxygen.
Which of the following is correct regarding pneumotoxic centres?
In HMP shunt, number of molecules of CO2 evolved are ______.
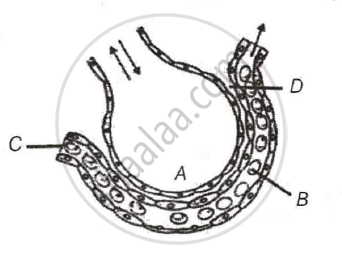
The figure given below shows a small part of human lung where exchange of gas takes place. In which one of the options given below, the one part A, B, C or D is correctly identified along with its function.
What is the vital capacity of our lungs?
Give function of carbonic anhydrase.
