Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Define Endocrine gland
Enlist human endocrine glands.
Solution 1
Endocrine glands, such as the thyroid, parathyroids, and adrenals, produce secretions that enter the bloodstream and trigger metabolic changes in specific organs. These glands lack ducts.
Solution 2
An organ that makes hormones that are released directly into the blood and travel to tissues and organs all over the body. Endocrine glands help control many body functions, including growth and development, metabolism, and fertility. Some examples of endocrine glands are the pituitary, thyroid, and adrenal glands.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Define the following:
Hormone
| Hormones | Target gland |
| Thyrotrophin (TSH) | ______ |
Give an example of gonadotrophic hormones.
add a note on deficiency of thyroxine.
_______ maintains basic metabolic rate.
(A) Thyroxine
(B) ADH
(C) GH
(D) Oxytocin
Fill in the blank:
Hormones are produced by ____________.
Identify the ODD term in each set and name the CATEGORY to which the remaining three belong :
Example : glucose, starch, cellulose, calcium
Odd term : calcium Category : others are different types of carbohydrates
Insulin, Adrenaline, Pepsin, Thyroxine
Which one of the following statement is true/ false?
Islets of Langerhans are found in the brain.
Name the hormones secreted by the following glands:
(i) Anterior pituitary
(ii) Testes
(iii) Ovary
(iv) Adrenal cortex
(v) Pancreas
Name the hormone responsible for the following function:
Regulates the functioning of the male and female reproductive organs
Name the hormone responsible for the following function:
Increased reabsorption of water in the kidneys
Choose the correct answer:
Which one of the following is not an endrocine gland?
Choose the correct answer:
Corpus luteum produces ____________
Why are hormones called ‘chemical messengers’?
Hormones are called ‘chemical messengers’.
The release of progesterone in the urine is an indication of pregnancy. Explain.
Differentiate: Cretinism and Myxedema.
Name the Following: Hormone secreted by corpus luteum.
Give the Technical Term: What are the substances that control the growth and development in animals?
Fill in the Blanks:
The glands with ducts are called ______.
Place the words at the bottom of the page next to the number that shows the location of the Endocrine Glands.

(1) ________
(2) ________
(3) ________
(4) ________
(5) ________
(6) ________
(7) ________
(8) ________
(9) ________
Pancreas Hypothalamus Pituitary Parathyroid Ovaries Adrenal Thyroid Thymus Testes
Some of the endocrine glands are shown by the guidelines.

(i) Name the glands 1 to 5.
(ii) Name any two endocrine glands which are not shown in the diagram.
(iii) Name one gland which is both exocrine and endocrine.
Study the diagram given below and then answer the questions that follow:
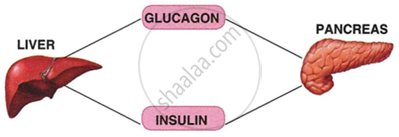 |
- Name the cells of the pancreas that produce (1) glucagon (2) insulin.
- State the main function of (1) glucagon and (2) insulin.
- Why is the pancreas referred to as an exo-endocrine gland?
- Why is insulin not given orally but is injected into the body?
- What is the technical term for the cells of the pancreas that produce endocrine hormones?
- Where in the body is the pancreas located?
Choose the Odd One Out
Column ‘II’ is a list of items related to ideas in Column ‘I’. Match the term in Column ‘II’ with a suitable idea given in Column ‘I’.
| Column A | Column B |
| (i) Pituitary | (a) produces male sex characteristics |
| (ii) Ovaries | (b) decreases blood sugar level |
| (iii) Thyroid | (c) increases heart and breathing rate raises blood pressure |
| (iv) Thymus | (d) produces female sex characteristics |
| (v) Adrenals | (e) is known as emergency hormone |
| (vi) Hypothalamus | (f) regulates the level of calcium and phosphorus |
| (vii) Pancreas | (g) increases the rate of metabolism |
| (viii) Testes | (h) maintains the level of calcium |
| (ix) Parathyroid | regulates the amount of water excreted in the urine. |
| (x) Cretinism | (j) simulates skeletal growth |
| (xi) Diabetes mellitus | (k) regulates the activities of other glands |
| (xii) Insulin shock | (l) stimulates the development of male and female sex organs |
| (xiii) Gigantism | (m) Shortage of glucose in the blood. |
| (xiv) Enlargement of breasts in adult males | (n) Over-secretion of growth hormone |
| (xv) Exophthalmic goiter | (o) Excess of glucose in the blood |
| (xvi) Acromegaly | (p) Over-secretion of thyroxin |
| (xvii) Addison’s disease | (q) Dwarfism and mental retardation |
| (xviii)Cretinism | (r) Over-secretion of cortical hormones |
| (xix) Dwarfism | (s) Under-secretion of the adrenal cortex |
| (xx) Adrenalin | (t) Under-secretion of thyroxin in children |
| (xxi) Vasopressin | (u) Over-secretion of growth hormones in adults |
Write the role of oestrogen in ovulation?
Pineal gland is an endocrine gland, write its role.
Comment on the functions of adrenalin.
Predict the effects of removal of pancreas from the human body.
Which endocrine gland is present in males but not in females?
