Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the change in demand of a good on account of change in prices of related goods.
Solution
Effect of change in the price of related goods:
i. Demand for a commodity in relation to the price of the substitute good
When the price of one good fall, it becomes cheaper in relation to another good. As a result, one good is substituted for the other good such as coffee and tea. Assume tea and coffee are two substitute goods. D1 is the demand curve for the demand of tea in diagram (a).
Increase in price of the substitute good:
When the price of tea is OP1, the quantity demanded is OT1 as shown in diagram (a). If there is an increase in the price of the substitute good coffee, then the demand curve for tea shifts to the right. Now, the consumer is willing to buy the P1C2 quantity of tea which is equal to OT2. Greater the purchase of a commodity at its constant price points to a situation of increase or forward shift in the demand curve. The consumer demand curve shifts from D1 to D2, consuming more of tea even when its price is constant.
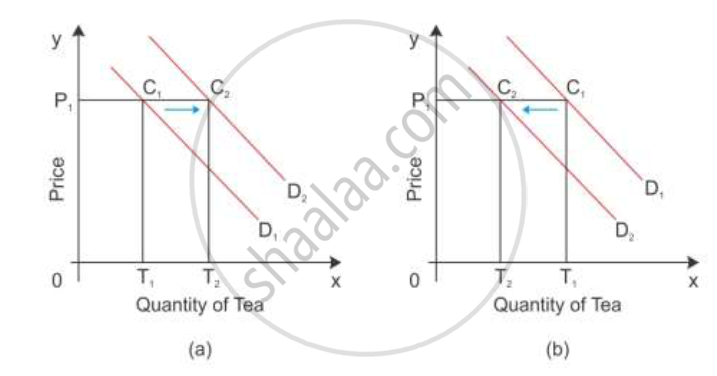
A decrease in the price of the substitute good:
When there is a decrease in the price of the substitute good coffee, the demand curve for
tea shifts to the left even when its price is constant. When the price of tea is OP1, the
quantity demanded is OT1 as shown in diagram (b). Now, the consumer is willing to buy
The P1C2 quantity of tea which is equal to OT2. Thus, the consumer shifts from D1 to D2,
consuming less of tea even when the price of tea is constant. This is a situation of the backward
shift in the demand curve.
ii. Demand for a commodity in relation to the price of the complementary good
Complementary goods are purchased jointly such as ink and ink pens.
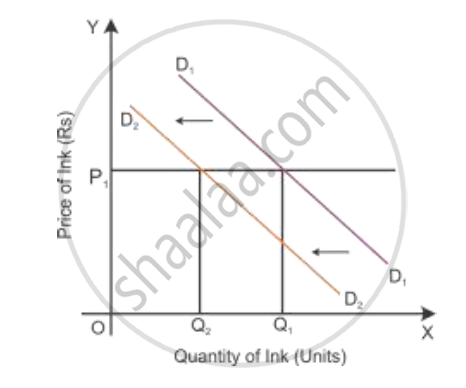
Increase in price of the complementary good:
If there is an increase in the price of a good, then the demand for another goodwill decline. So
the demand curve shifts parallel to the left, i.e. from D1D1 to D2D2.
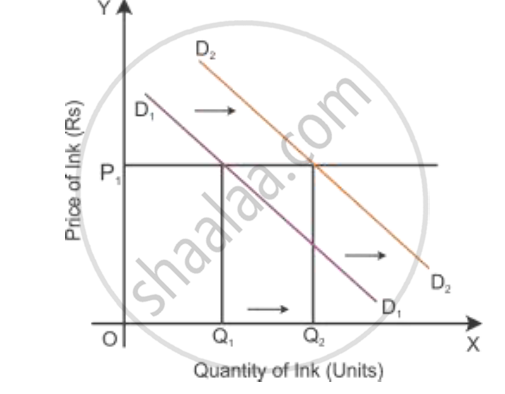
A decrease in the price of the complementary good:
If there is a decrease in the price of a good, then the demand for another good will increase. So
the demand curve shifts parallel to the right, i.e. from D1D1 to D2D2
RELATED QUESTIONS
When is the demand for a good said to be inelastic?
Income of the buyers and demand for a good.
Give reasons or Explain the following statements.
All desires are not demand.
State whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE with reason.
The demand for consumption goods is direct demand.
Choose the correct answer :
The demand of a salt is _________.
State Whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE:
Demand will not increase by coming of new customers.
State Whether the following statements are TRUE or FALSE:
Demand elasticity concept is useful for labour unions.
Choose the correct answer :
Demand elasticity of habitual goods is _________.
Suppose the price elasticity of demand for a good is −0.2. If there is a 5% increase in the price of the good, then by what percentage will the demand for the good go down?
Suppose the price elasticity of demand for a good is −0.2. How will the expenditure on the good be affected if there is a 10% increase in its price ?
Suppose there was a 4% decrease in the price of a good, and as a result, the expenditure on the good increased by 2%. What can you say about the elasticity of demand ?
Distinguish between:
Increase in demand and Decrease in demand
Distinguish between:
Increase in demand and Decrease in demand
