Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain chromatic aberration for spherical lenses.
Solution
- Lenses are prepared by using a transparent material medium having a different refractive index for different colours. Hence angular dispersion is present.
- If the lens is thick, this will result in notably different foci corresponding to each colour for a polychromatic beam, like a white light. This defect is called chromatic aberration.
- As violet light has maximum deviation, it is focussed closest to the pole.
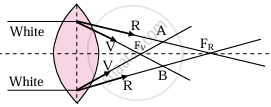
(a) Chromatic aberration in convex lens
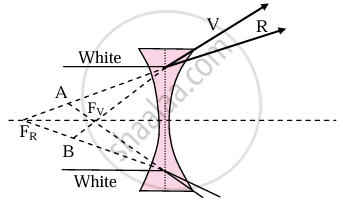
(b) Chromatic aberration in concave lens
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question.
Explain spherical aberration for spherical mirrors. How can it be minimized? Can it be eliminated by some curved mirrors?
Answer the following question in detail.
What is achromatism? Derive a condition to achieve achromatism for a lens combination. State the conditions for it to be converging.
Answer the following question in detail.
Describe spherical aberration for spherical lenses. What are the different ways to minimize or eliminate it?
Answer the following question in detail.
Derive the expressions for the magnifying power and the length of a compound microscope using two convex lenses.
Refractive index of a flint glass varies from 1.60 to 1.66 for visible range. Radii of curvature of a thin convex lens are 10 cm and 15 cm. Calculate the chromatic aberration between extreme colours.
Refractive index of a flint glass varies from 1.60 to 1.66 for visible range. Radii of curvature of a thin convex lens are 10 cm and 12 cm. The chromatic aberration between extreme colours is ____________.
A convex lens of focal length 'f' is placed in contact with a concave lens of the same focal length. The equivalent focal length of the combination is ______.
Focal length of a convex lens will be minimum for ______.
The equiconvex lens has a focal length 'f'. If the lens is cut along the line perpendicular to principal axis and passing through the pole, what will be the focal length of any half part?
A glass slab of thickness 4 cm contains the same number of waves as in 'x' cm of water column when both are traversed by the same monochromatic light. If the refractive indices of glass and water for that light are `5/3` and `4/3` respectively, the value of x will be ______.
