Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain dielectrics in detail and how an electric field is induced inside a dielectric.
Solution
When an external electric field is applied on a conductor, the charges are aligned in such a way that an internal electric field is created which cancels the external electric field. But in the case of a dielectric, which has no free electrons, the external electric field only realigns the charges so that an internal electric field is produced.
The magnitude of the internal electric field is smaller than that of the external electric field. Therefore the net electric field inside the dielectric is not zero but is parallel to an external electric field with a magnitude less than that of the external electric field. For example, let us consider a rectangular dielectric slab placed between two oppositely charged plates (capacitor) as shown in the figure.
(a) Randomly oriented polar molecules-
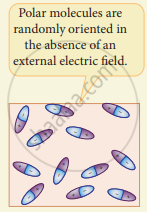
(b) Align with the external electric field-
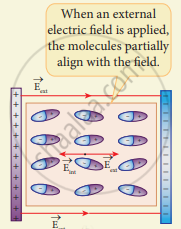
The uniform electric field between the plates Induced electric field lines inside the dielectric acts as an external electric field `vec"E"_"ext"` which polarizes the dielectric placed between plates. The positive charges are induced on one side surface and negative charges are induced on the other side of surface But inside the dielectric, the net charge is zero even in a small volume. So the dielectric in the external field is equivalent to two oppositely charged sheets with the surface charge densities +σb and -σb. These charges are called bound charges. They are not free to move like free electrons in conductors. This is shown in the figure.

(a) Balloon sticks to the wall

(b) Polarisation of wall due to the electric field created by the balloon
For example, the charged balloon after rubbing sticks onto a wall. The reason is that the negatively charged balloon is brought near the wall, it polarizes opposite charges on the surface of the wall, which attracts the balloon.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write a short note on ‘electrostatic shielding’.
What is polarisation?
What is dielectric strength?
Discuss the various properties of conductors in electrostatic equilibrium.
Explain the process of electrostatic induction.
An electron and a proton are allowed to fall through the separation between the plates of a parallel plate capacitor of voltage 5 V and separation distance h = 1 mm as shown in the figure.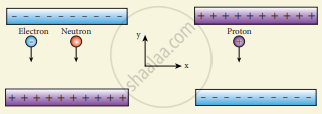
- Calculate the time of flight for both electron and proton.
- Suppose if a neutron is allowed to fall, what is the time of flight?
- Among the three, which one will reach the bottom first?
(Take mp = 1.6 x 10-27 kg, me= 9.1 x 10-31 kg and g = 10 m s-2)
