Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the geometric method of measuring price elasticity of supply. Use Diagram.
Solution
The geometric method measures elasticity at a given point on the supply curve and is also
known as ‘Arc method’ or Point method’.
At point ‘A’, the price is OP and the quantity supplied is OQ. When the price rises to OP1,
quantity supplied also raise to OQ1. The supply curve is extended beyond the Y-axis, so
that it meets the extended X-axis at point ‘L’ now, at point A, an elasticity of supply is equal to:
`E_S = (ΔQ)/(ΔP) xx P/Q`
Given
`ΔQ = QQ_1;ΔP = PP_1; P = 0 P and Q = OQ`
Substituting these values in the formula, we get
`E_S = ("QQ"_1)/(PP_1) xx (OP)/(OP)`
QQ1 = AC;PP1 = BC and OP = AQ.
Substituting these values in the above equation, we get
`E_S = (AC)/(BC) xx (AQ)/(OQ)`
Now, ΔBAC and ΔALQ are similar triangles on account of AAA property.
The ratio of their sides will be equal. It implies that
`(AC)/(BC) = (LQ)/(AQ)`
Substituting the value, we get :
`E_S = (LQ)/(AQ) xx (AQ)/(OQ)` or
`E_S = (LQ)/(OQ) = "Intercept on X-axis"/"Quantity Supplied at that price"`
Three different cases of Geometric Method
1) Highly Elastic Supply (Es > 1)
A supply curve, which passes through the Y-axis and meets the extended X-axis at some point (say, L in Figure) , then supply is highly elastic. In
Elasticity of supply `(E_S) = (LQ)/(OQ)` and LQ > OQ
Since LQ > OQ, the elasticity of supply at point A > 1 (Es >1).

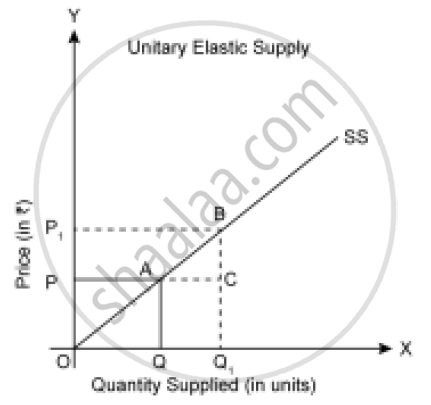
2) Unitary Elastic Supply (Es =1)
If the straight line supply curve passes through the origin, then the elasticity of supply will be equal to one `E_S = (OQ)/(OQ) = 1`
Hence, the supply is unitary elastic.
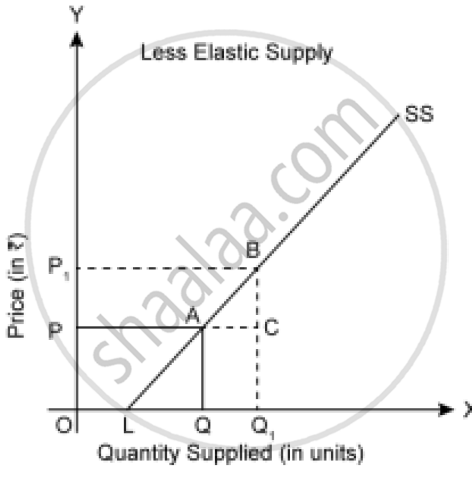
3) Less Elastic Supply `(E_S > 1)`
If a supply curve meets the x-axis at some point say L, then supply is less elastic.
`E_S = (LQ)/(OQ)` and LQ < OQ.
Hence, supply is less elastic `E_S < 1`
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
The price elasticity of supply of a good is 0.8. Its price rises by 50 percent. Calculate the percentage increase in its supply.
Total revenue is Rs 400 when the price of the commodity is Rs 2 per unit. When price rises to Rs 3 per unit, the quantity supplied is 300 units. Calculate the price elasticity of supply.
The price of a mobile handset has risen in the market. But the dealers have not been able to increase the supply proportionately.
What will be the price elasticity of supply for the mobile handset? Draw the supply curve to indicate the type of elasticity.
