Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain how the interference of waves is formed.
Solution
Interference is a phenomenon in which two waves superimpose to form a resultant wave of greater, lower, or the same amplitude.
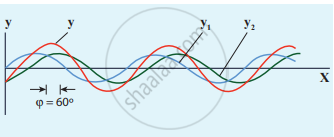
Interference of two sinusoidal waves
Let us consider two harmonic waves having identical frequencies, constant phase difference φ, and same waveform (can be treated as coherent source), but having amplitudes A1 and A2, then
y1 = A1 sin(kx – ωt) … (1)
y2 = A2 sin(kx – ωt) … (2)
Suppose they move simultaneously in a particular direction, then interference occurs (i.e., the overlap of these two waves). Mathematically y = y1 + y2 … (3)
Hence by substituting equation (1) and equation (2) in equation (3), we get
y1 = A1 sin(kx − ωt)
y2 = A2 sin(kx − ωt + φ)
y = `{("A"_1 sin (k"x" - omega"t")),(+ "A"_2 sin(k"x" - omega"t" + φ)):}`
Using trigonometric identity
sin (α + β) = (sin α cos β + cos α sin β), we get
y = `{("A"_1 sin (k"x" - omega"t")),(+ "A"_2 sin(k"x" - omega"t" + φ)),(+ cos (k"x" - omega"t") sin φ):}`
y = `{(sin (k"x" - omega"t")("A"_1 + "A"_2 cos φ)),(+ "A"_2 sin φ cos (k"x" - omega"t")):}` ...(4)
Let us re-define
A cos θ = (A1 + A2 cos φ) ....(5)
and A sin θ = A2 sin φ ....(6)
then equation (4) can be rewritten as
y = `{("A" sin (k"x" - omega"t") cos theta),(+ "A" cos(k"x" - omega"t")sin theta):}`
y = `{("A" sin (k"x" - omega"t") cos theta),(+ sin theta cos(k"x" - omega"t")):}`
y = A sin (kx - ωt + θ) ....(7)
By squaring and adding equation (5) and (6), we get,
A² = A1² + A2² + 2A1A2cosφ … (8)
Since, intensity is square of the amplitude (I – A²), we get,
I = I1 + I2 + 2`sqrt("I"_1"I"_2)`cos φ ....(9)
This means the resultant intensity at any point depends on the phase difference at that point.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
An organ pipe A closed at one end is allowed to vibrate in its first harmonic and another pipe B open at both ends is allowed to vibrate in its third harmonic. Both A and B are in resonance with a given tuning fork. The ratio of the length of A and B is
What is meant by interference of waves?
Explain the beat phenomenon.
Briefly explain the concept of the superposition principle.
Describe the formation of beats.
