Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain how will you predict the direction of an equilibrium reaction.
Solution
From the knowledge of the equilibrium constant, it is possible to predict the direction in which the net reaction is taking place for a given concentration or partial pressure of reactants and products.
Consider a general homogeneous reversible reaction,
xA + yB ⇌ lC + mD
For the above reaction under non-equilibrium conditions, reaction quotient ‘Q’ is defined as the ratio of the product of active masses of reaction products raised to the respective stoichiometric coefficients in the balanced chemical equation to that of the reactants.
Under non – equilibrium conditions, the reaction quotient Q can be calculated using the following expression.
Q = `(["C"]^1["D"]^"m")/(["A"]^"x"["B"]^"y")`
As the reaction proceeds, there is a continuous change in the concentration of reactants and products and also the Q value until the reaction reaches equilibrium. At equilibrium, Q is equal to Kc at a particular temperature. Once the equilibrium is attained, there is no change in the Q value. By knowing the Q value, we can predict the direction of the reaction by comparing it with Kc.
If Q = Kc, the reaction is in an equilibrium state.
If Q > Kc, the reaction will proceed in the reverse direction, i.e., the formation of reactants.
If Q < Kc, the reaction will proceed in the forward direction i.e., formation of products.
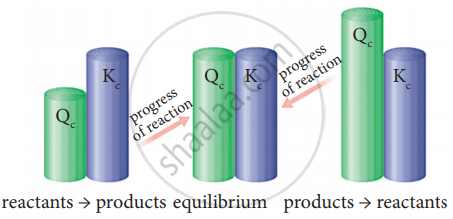
Predicting the direction of a reaction
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Mention various applications of equilibrium constant.
If x is the fraction of PCl5 dissociated at equilibrium in the reaction
\[\ce{PCl5 <=> PCl3 + Cl2}\]
then starting with 0.5 mole of PCl5, the total number of moles of reactants and products at equilibrium is
In the reaction
\[\ce{Fe(OH)3(S) <=> Fe^{(3+)} (aq) + 3OH- (aq)}\]
if the concentration of OH– ions is decreased by 1/4 times, then the equilibrium concentration of Fe3+ will
Equimolar concentrations of H2 and I2 are heated to equilibrium in a 1 liter flask. What percentage of the initial concentration of H2 has reacted at equilibrium if the rate constant for both forward and reverse reactions are equal
Consider the following reversible reaction at equilibrium,
\[\ce{A + B <=> C}\],
If the concentration of the reactants A and B are doubled, then the equilibrium constant will
If there is no change in concentration, why is the equilibrium state considered dynamic?
For a reversible reaction, if the concentrations of the reactants are doubled, then the equilibrium constant value ______.
