Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the roles of the following with the help of an example each in recombinant DNA technology :
Restriction Enzymes
Solution
Restriction enzymes are specialised enzymes that recognise and cut a particular sequence of DNA. Every restriction enzyme identifies specific sequences called recognition sequences. These recognition sequences are palindromic. Palindromes are the sequence of base pairs that read same both backwards and forwards (i.e., same in 5' → 3' and 3' → 5' direction).
Restriction enzymes are of two types:
1) Restriction endonucleases − They cut the DNA at specific positions within the DNA
2) Restriction exonucleases − They cut the DNA at the ends (remove the nucleotides at the ends of the DNA).
The restriction endonuclease is specifically important and is extensively used in recombinant DNA technology. They are capable of cutting DNA fragment in two ways, resulting in the formation of either blunt or sticky ends. Sticky ends obtained after the action of restriction enzymes are particularly important in recombinant DNA technology as they are helpful in linking the foreign DNA to the vector.
Restriction enzymes cut a little away from the centre of the palindrome site, but between the two bases on opposite strands. For example, restriction enzyme Eco-RI is one such restriction endonuclease that gives sticky ends.
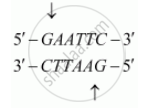
Hence, structures called overhangs (or sticky ends) are generated on each strand. Overhangs are the structures obtained after palindromic sequences are cut by molecular scissors.

They are significant because these sticky ends form hydrogen bonds with their complementary counterparts with the help of DNA ligases.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Why is the enzyme cellulase needed for isolating genetic material from plant cells and not form the animal cells?
Suggest a technique to a researcher who needs to separate fragments of DNA.
How does a restriction nuclease function? Explain
Answer the following question.
Explain the significance of palindromic nucleotide sequence in the formation of recombinant DNA.
The DNA fragment separated on an agarose gel can be visualized by staining with ______.
Molecular scissors, which cut DNA at specific site is ______.
While isolating DNA from bacteria, which of the following enzymes is not required?
A mixture of fragmented DNA was electrophoresed in an agarose gel. After staining the gel with ethidium bromide, no DNA bands were observed. What could be the reason?
CTTAAG
GAATTC
- What are such sequences called? Name the enzyme used that recognizes such nucleotide sequences.
- What is their significance in biotechnology?
What is elution?
