Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain sexual reproduction in plants.
Solution

- In sexually reproducing plants, flowers function as the reproductive organs.
- In flowers, male organ is the stamen and female organ is the carpel.
- Flowers which have both the male and female organs i.e. stamens and carpels are called bisexual flowers whereas flowers which have either male or female organs are called unisexual.
- Male gametes called pollen grains are produced by stamen, and carpels produce female gametes called ovules or egg cells inside ovaries.
- Fertilization takes place in the ovule where the egg cell and pollen grain fuse.
- This fertilized egg cell later develops into an embryo and the entire ovule gets converted into a seed.
- Under favourable conditions, the seed germinates to give rise to a new plant.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Answer the following question.
What is pollination? Explain the different types of pollination.
How does fertilisation occur in flowers? Name the parts of the flower that develop into (i) seed, and (ii) fruit after fertilisation.
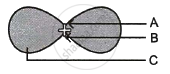
Name the parts A, B and C shown in the following diagram and state one function of each.

Name and differentiate between the two modes of pollination in flowering plants.
A student identified the various parts of an embryo of a gram seed and listed them as given below :
(I) Testa
(II) Plumule
(III) Radicle
(IV) Cotyledon
(V) Tegmen
Out of these the actual parts of the embryo are :
(A) I, II, III
(B) II, III, IV
(C) III, IV, V
(D) II, IV, V
Mention the changes a flower undergoes after fertilisation.
You are asked by your teacher to study the different parts of an embryo of a gram seed. Given below are the steps to be followed for the experiment:
I. Soak the gram seeds in plain water and keep them overnight.
II. Cut open a soaked seed and observe its different parts.
III. Take some dry gram seeds in a petri dish.
IV. Drain the excess water.
V. Cover the soaked seeds with a wet cotton cloth and leave them for a day.
The correct sequence of these steps is :
(A) III, I, V, IV, II
(B) III, I, II, IV, V
(C) III, IV, V, I, II
(D) III, I, IV, V, II
Explain what you understand by sexual reproduction.
Name the part made up of the stigma, style and ovary.
Name the male part of the flower.
What is the function of a flower?
What is the name of female organ of a flower (other than carpel)?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The.......... at the base of the carpel contains egg cells.
Explain the terms 'self pollination'
Name the part of a seed which contains stored food.
What is meant by 'unisexual flowers' and 'bisexual flowers'? Give two examples of each.
Put a tick mark (✓) against the correct alternative in the following statement
Pollen is produced in the:
Fill in the blank by selecting suitable word:
A flower that bears both the male and the female parts is known as __________ flower.
What is a flower ? Draw a neat labelled diagram showing the L.S. of a typical flower.
Fill in the blank:
Seeds are formed from________.
Draw a labelled diagram of a bisexual flower.
Write one main difference between asexual and sexual mode of reproduction. Which species is likely to have comparatively better chances of survival – the one reproducing asexually or the one reproducing sexually? Give reason to justify your answer.
The students of a class were asked by the teacher to study the different parts of an embryo of an angiosperm. Given below are the essential steps for the experiment :
A. Soak the seeds in plain water and keep them overnight.
B. Cut open the soaked seed and observe its different parts.
C. Take some healthy seeds in a petri-dish.
D. Drain the excess water, cover the seeds with a wet cotton cloth and leave them as it is for a day.
The correct sequence of these steps is
(a) C, A, D, B
(b) C, D, A, B
(c) A, C, D, B
(d) A, C, B, D
What is phototropism?
Describe an activity to demonstrate phototropism.
Fill in the blank by selecting suitable word:
Transfer of pollen grains from the anther to the stigma is known as______________.
Draw a diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower and label the following parts.
Calyx : Sepals : : Corolla : ________________
Pollen tube reaches the embryo sac via style.
Give scientific reason.
Flower is a structural unit of sexual reproduction in plants.
Explain the sexual reproduction process in plants with a diagram.
Where does the endothecium layer of anther lobes is present?
The anther wall consists of four wall layers where ______
Generally, in a pollen tube, which of the following moves to the tip of the tube?
Which type of development is observed in male gametophytes of plants?
The process of release of eggs from the ovary is called ______
Which out of the following processes does not lead to the formation of clones.
Type of sexual reproduction is ______.
Given below is a diagram of a germinating seed. Label the parts that:
- gives rise to future shoot.
- gives rise to future root system.
- stores food.