Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the following, giving two examples:
Coordination polyhedron
Solution
The spatial arrangement of the ligand atoms, which are directly attached to the central atom/ion, defines a coordination polyhedron about the central atom. The most common coordination polyhedra are octahedral, square planar and tetrahedral. For example, [Co(NH3)6]3+ is octahedral, [Ni(CO)4] is tetrahedral and [PtCl4]2− is square planar.
RELATED QUESTIONS
Give the oxidation state, d-orbital occupation and coordination number of the central metal ion in the following complex:
[Mn(H2O)6]SO4
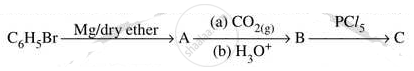
Write structures of compounds A, B and C in of the following reactions
Following compounds are given to you :
2-Bromopentane, 2-Bromo-2-methylbutane, 1-Bromopentane
1) Write the compound which is most reactive towards SN2 reaction.
2) Write the compound which is optically active.
3) Write the compound which is most reactive towards β-elimination reaction.
The oxidation number of Fe in K4[Fe(CN)6] is ____________.
Arrange the following complexes in the increasing order of conductivity of their solution:
[Co(NH3)3Cl3], [Co(NH3)4Cl2]Cl, [Co(NH3)6]Cl3, [Cr(NH3)5Cl]Cl2
Which one of the following does not achieve an octet of electrons in the central atom?
The complex which has no d electrons in the central atom is:-
The one that will show optical activity is: (en = ethane 1, 2-diamine)
Does ionization isomer for the following compound exist? Justify your answer.
\[\ce{Hg[Co(SCN)4]}\]
What is meant by the chelate effect? Give an example.
