Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the following process:
Transmission of a nerve impulse across a chemical synapse
Solution 1
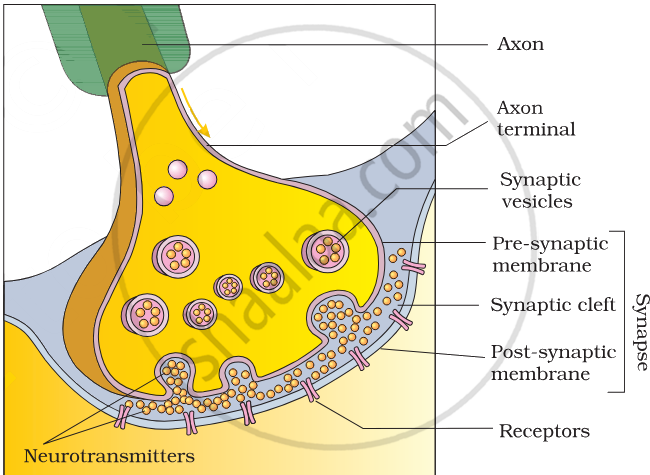
- A nerve impulse is sent across a chemical synapse, which is a fluid-filled gap between the membranes of pre- and post-synaptic neurons known as the synaptic cleft. These synapses use chemicals known as neurotransmitters to convey impulses. These neurotransmitters are stored in vesicles at the axon terminals.
- When an impulse (action potential) arrives at the axon terminal, it stimulates synaptic vesicles to migrate towards the membrane, where they fuse with the plasma membrane and burst, releasing neurotransmitters into the synaptic cleft.
- The released neurotransmitters bind to certain receptors found on the post-synaptic membrane. This interaction opens ion channels, allowing ions to enter and generate a new potential in the postsynaptic neuron. The new potential created can be either excitatory or inhibitory.
Solution 2
- There is a synapse between the end button located at the end of the axon and the dendrite of another nerve cell.
- Therefore, transmission of impulses at this place takes place through a special chemical substance called a neurohormone called acetylcholine.
- On receiving the impulse, the secretory vesicles present in the end button secrete acetylcholine. This substance establishes the functional potential in the dendrite of the second nerve cell.
- Now this potential, in the form of an impulse, continues to move forward along the entire length of the next nerve fibre.
- Thus, acetylcholine acts like a chemical messenger. Later, acetylcholine is degraded by the coenzyme acetylcholinesterase.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the role of Na+ in the generation of action potential.
Long answer question.
Explain the process of conduction of nerve impulses up to the development of action potential.
Dendrites transmit impulse ______ cell body and axon transmit impulse ______ cell body.
What are the number of Na+ ions pumped out, and K+ ions pumped into the cell, with respect to the Na+ - K+ pump?
Match the Column - I with Column - II:
| Column I | Column II | ||
| i. | P - wave | p. | Depolarisation of ventricles |
| ii. | QRS complex | q. | Repolarisation of ventricles |
| iii. | T - wave | r. | Coronary ischemia |
| s. | Development of atria | ||
| t. | Repolarisation of atria |
Neurotransmitters are removed from synaptic cleft by ____________ after transmission of impulse.
Under which of the following conditions will the ionic gradients across the resting membrane be maintained?
Which of the following is TRUE for the external tissue fluid in polarized state?
Which of the following situations is responsible for resting membrane potential?
Identify the correct path of transmission of nerve impulse.
Which of the following statements is TRUE for medullated nerve fibre?
When stimulus is applied to a membrane of neuron, it causes rapid influx of ____________.
Potential difference across resting membrane is negative. This is due to differential distribution of the following ions ______.
Complete the statement by choosing appropriate match among the following -
| a. Resting potential | i. Chemicals involved in the transmission of impulses at synapses. |
| b. Nerve impulse | ii. Gap between the pre synaptic and post synaptic neurons |
| c. Synaptic cleft | iii. Electrical potential difference across the resting neural membrane |
| d. Neurotransmitters | iv. An electrical wave like response of a neuron to a stimulation |
The electronegativity inside the membrane is due to
Write a short note on the following:
Synapse
