Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the following processes:
Conduction of a nerve impulse along a nerve fibre
Solution 1
Conduction of a nerve impulse along a nerve fibre: Nervous system transmits information as a series of nerve impulses. A nerve impulse is the movement of an action potential as a wave through a nerve fibre. Action potentials are propagated, that is, self-generated along the axon. The events that set up an action potential at one spot on the nerve fibre also transmit it along the entire length of the nerve fibre. The action potential then moves to the neighbouring region of the nerve fibre till it covers the whole length of the fibre.
Solution 2
Conduction of a nerve impulse along a nerve fibre
There are two types of nerve fibres – myelinated and non-myelinated. In myelinated nerve fibre, the action potential is conducted from node to node in jumping manner. This is because the myelinated nerve fibre is coated with myelin sheath. The myelin sheath is impermeable to ions. As a result, the ionic exchange and depolarisation of nerve fibre is not possible along the whole length of nerve fibre. It takes place only at some point, known as nodes of Ranvier, whereas in non-myelinated nerve fibre, the ionic exchange and depolarization of nerve fibre takes place along the whole length of the nerve fibre. Because of this ionic exchange, the depolarized area becomes repolarised and the next polarized area becomes depolarized.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Briefly describe the structure of the Brain.
Briefly describe the Given structure - Ear
Compare the following:
Central neural system (CNS) and Peripheral neural system (PNS)
Explain the following process:
Depolarisation of the membrane of a nerve fibre.
Write short note on the following:
Neural coordination
Distinguish between Afferent neurons and efferent neurons.
Examine the diagram of the two cell types A and B given below and select the correct option.
The respiratory centre is present in the ______.
The abundant intracellular cation is ______.
Several statements are given here in reference to cone cells which of the following option indicates all correct statements for cone cells?
Statements
- Cone cells are less sensitive in bright light than Rod cells
- They are responsible for colour vision
- Erythropsin is a photo pigment which is sensitive to red colour light
- They are present in fovea of retina
Which of the following statement concerning the somatic division of the peripheral neural system is incorrect?
Pleasant smell of food urged Ravi to rush into the kitchen. Name the parts of the brain involved in the identification of food and emotional responses to odour.
The choroid plexus secretes cerebrospinal fluid. List the function of it.
What is ANS? Explain the components of ANS.
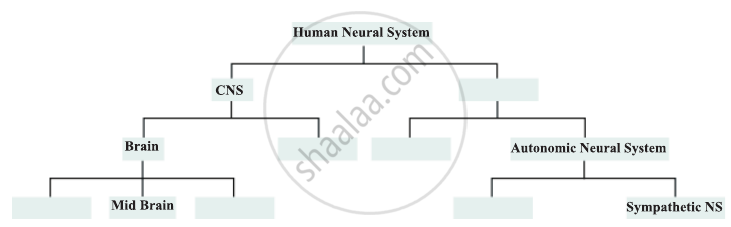
The major parts of the human neural system is depicted below. Fill in the empty boxes with appropriate words.
If someone receives a blow on the back of neck, what would be the effect on the person’s CNS?
