Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the law of demand and its exceptions.
Solution
The law of demand was first stated by Augustin Cournot in 1838. Later it was refined and elaborated by Alfred Marshall.
Definition:
The law of demand says as “The quantity demanded increases with a fall in price and diminishes with a rise in price” -Marshall
Assumptions of the law:
- The income, taste, habit, and preference of the consumer remain the same.
- No change in the prices of related goods.
- No substitutes for the commodity.
- The demand for the commodity must be continuous.
- No change in the quality of the commodity.
If there is change even in one of these assumptions, the law will not operate.
Demand schedule:
| Price (Rs) | Quantity Demanded |
| 5 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
| 2 | 4 |
| 1 | 5 |
From the above schedule if the price of the good is 5 then the quantity demanded is 1 unit and if the price decrease to 1 quantity demanded raises to 5 which shows the inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded.
Diagram:
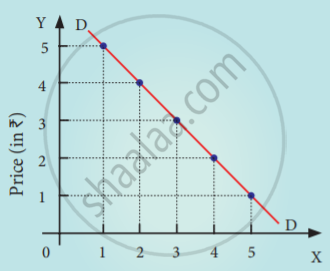
Quantity Demanded (in units)
In the above diagram, X-axis represents the quantity demanded and Y-axis represents the price. DD is the demand curve that has a negative slope. It indicates that when the price falls, the demand expands and when the price rises, the demand contracts.
Market demand for a commodity: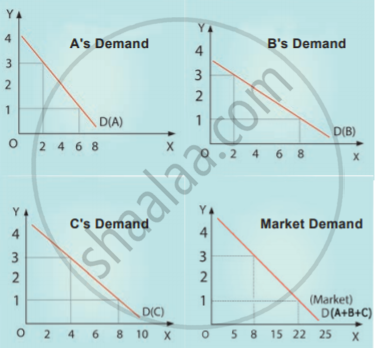
The market demand curve for a commodity is derived by adding the quantum demanded of the
commodity by all the individuals in the market.
Exceptions to the law of demand:
- There are some unusual demand curves that slope upwards from left to right. It is known as the exceptional demand curve.
- In the case of an exceptional demand curve, a fall in price brings about contraction, and a rise in price brings about the extension of demand.
Reasons for exceptional demand curve:
- Giffen paradox
- Veblen or demonstration
- Ignorance
- Speculative effect
- Fear of shortage
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Briefly explain any two reasons for the occurrence of the law of demand.
The Law of Demand was introduced by ______.
State with reason whether you agree or disagree with the following statement.
There is an inverse relationship between price and demand.
Increase in demand is caused by
The movement on or along the given demand curve is known as ______
Distinguish between extension and contraction of demand.
Write a statement of the Law of Demand.
State with reason whether you agree or disagree with the following statement :
When price of Giffen goods fall, the demand for it increases.
State and explain the law of demand with the help of a hypothetical schedule and graph.
Any statement about demand for a good is considered complete only when the following is/are mentioned in it:
When at a price of ₹ 5 per unit of a commodity, A's demand is for 11 units, B's demand is for 14 units and C's demand is for units (assuming that there are only three consumers in the market), the market demand is ______.
Giffen goods are richman's goods
If prices of cars rise, many people may put off buying a new car. So the demand for petrol will fall.
If a good is inferior good, then purchases of that good will decrease when ______.
State the law of demand.
Explain four circumstances under which the law of demand does not operate.
The following table shows the amount of sugar bought by a household at different prices:
| Period | Price (₹ per kg) | Amount Bought (kg) |
| Jan. 2000 | ₹ 15 | 4 |
| Feb. 2000 | ₹ 16 | 5 |
Does the behaviour of household contradict the law of demand? Give reasons in support of your answer.
