Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain the term inductive reactance. State its unit and dimensions.
Solution
- The opposing nature of an inductor to the flow of alternating current is called inductive reactance.
- In an inductive circuit,
i0 = `"e"_0/(omega"L")` ….(1) - For a resistive ac circuit, according to Ohm’s law,
i = `"V"/"R"` ….(2)
where R = resistance in the circuit - Comparing equations (1) and (2), we can conclude that ωL plays a similar role in an inductive ac circuit as a resistor in a pure resistor circuit.
- Hence, the effective resistance XL offered by the inductance L is called inductive reactance and is given as,
XL = ωL = 2πfL. .......….(∵ ω = 2π/T = 2πf)
where f = frequency of the AC supply. - XL is directly proportional to the inductance (L) and the frequency (f) of the alternating current.
- In DC circuits, f = 0
∴ XL = 0
It implies that a pure inductor offers zero resistance to DC, i.e., it cannot reduce DC.
Thus, it passes DC and blocks AC of very high frequency. - In an inductive circuit, the self-induced emf opposes the growth as well as decay of current.
- The dimensions of inductive reactance are [ML2T-3I -2] and its SI unit is the ohm (Ω).
RELATED QUESTIONS
Choose the correct option.
If the rms current in a 50 Hz AC circuit is 5A, the value of the current 1/300 seconds after its value becomes zero is ______.
In an AC circuit, e and i are given by e = 150 sin(150t)V and i = 150 sin `(150t + π/3)` A. The power dissipated in the circuit is ______.
An electric lamp is connected in series with a capacitor and an AC source is glowing with a certain brightness. How does the brightness of the lamp change on increasing the capacitance?
If AC voltage is applied to a pure capacitor, then the voltage across the capacitor ______
An electric bulb operates 10 V d.c. If this bulb is connected to an a.c. source and gives normal brightness, then the peak value of the source is ______
A coil of resistance 300Ω and inductance 1.0 H is connected across an alternating voltage of frequency `300/(2pi)` Hz, therefore phase difference between the voltage and current in the circuit is ______
Define capacitive reactance.
State the equation for impedance Z in an A.C. circuit.
If the peak value of an alternating emf is 15V, what is its mean value over half cycle?
Explain term impedance and state the formula for it in the case of an LCR series circuit.
A series LCR circuit has resistance 10Ω and reactance is `7sqrt2` Ω. What is the impedance of the circuit?
Find the current in a circuit consisting of a coil and a capacitor in series with an A.C source of 110V (r.m.s.), 60Hz. The inductance of a coil is 0.80 H and its resistance is 50Ω. The capacitance of a capacitor is 8µF.
A 0.5µF capacitor is discharged through a 10 millihenry inductor. Find the frequency of discharge.
What is the capacitive reactance of a capacitor of 5µF at a frequency of (1) 50 Hz and (2) 20KHZ?
Obtain the expression for the applied emf and the effective resistance of the circuit when alternating emf is applied to a CR circuit.
The standard voltage of A.C. mains in India is ______
For circuit shown in figure IE = 4 mA, IB = 40 µA. What are the values of ex, and le respectively?
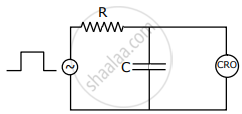
An RC Circuit as shown in the figure is driven by a AC source generating a square wave. The output wave pattern monitored by CRO would look close to:
A telegraph line of length 100 km has a capacity of 0.01 µF/ km and it carries an alternating current at 0.5 kilo cycle per second. If minimum impedance is required, then the value of the inductance that needs to be introduced in series is ______ mH. (if π = `sqrt10`)
