Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Explain why an indifference curve is downward sloping from left to right.
Explain why is an indifference curve is Downward-sloping
Why does the indifference curve slope downward?
Solution 1
The indifference curves slope downwards because an increase in the amount of Good 1 along the indifference curve is associated with a decrease in the amount of Good 2, as the preferences are monotonic.
Solution 2
An indifference curve slopes downward from left to right, i.e., it has a negative slope. This property is based on the assumption that if a consumer consumes more of one commodity (food), he must consume less quantity of the other (clothing), then only he will have the same level of satisfaction from different combinations of the two commodities. This follows from the assumption of non-satiety. For example, Fig. 4 illustrates that when the consumers move from combination 'A' to combination 'B' on the given indifference curve (IC), he consumes 1 more unit of food, but 3 units less of clothing so as to get the same level of satisfaction from both the combinations. This necessitates that an indifference curve must be negatively sloped. However, if the amount of food is increased and the amount of clothing remains the same, the consumer will prefer new combination to the initial one because the new combination will give him more utility. Therefore, these two combinations will not lie on the same indifference curve.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the conditions of consumer’s equilibrium using indifference curve analysis.
Explain the three properties of the indifference curves.
Define an indifference curve.
Why is an indifference curve negatively sloped? Explain.
If Marginal Rate of Substitution is constant throughout, the Indifference curve will be :(choose the correct alternative)
a. Parallel to the x-axis.
b. Downward sloping concave.
c. Downward sloping convex.
d. Downward sloping straight line.
If Marginal Rate of Substitution is increasing throughout, the Indifference Curve will be: (Choose the correct alternative)
a. Downward sloping convex
b. Downward sloping concave
c. Downward sloping straight line
d. Upward sloping convex
A consumer consumes only two goods. If the price of one of the goods falls, the indifference curve: (Choose the correct alternative)
a. Shifts upwards
b. Shifts downwards
c. Can shift both upwards or downwards
d. Does not shift
Define an indifference map. Why does indifference curve to the right show more utility? Explain.
What are the properties of indifference curves?
Identify the correct pair of items from the following Columns I and II:
| Columns I | Columns II |
| (1) Demand Curve | (a) Downward sloping |
| (2) Indifference curve | (b) Upward rising |
| (3) Marginal Utility Curve | (c) L shaped curve |
| (4) Total Utility Curve | (d) Y shaped curve |
Which of these is not a property of indifference curve?
"Higher indifference curve represents fewer quantities of one or both goods, a higher indifference curve shows higher utility level." Choose the correct option for the above mentioned statement:
Indifference curve is:
Which of the following is an assumption for Indifference Curve Approach.
Which of the following statements are incorrect?
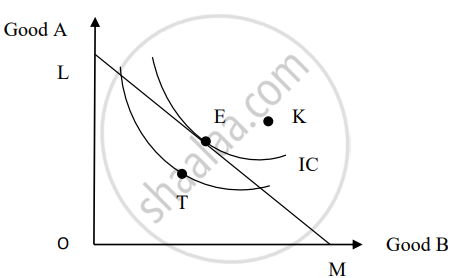
Points K and T will NOT be attained by the consumer. Select the reason from the options given below.
