Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain why a brass tumbler feels much colder than a wooden tray on a chilly day
Solution 1
Brass is a good conductor of heat. When one touches a brass tumbler, heat is conducted from the body to the brass tumbler easily. Hence, the temperature of the body reduces to a lower value and one feels cooler.
Wood is a poor conductor of heat. When one touches a wooden tray, very little heat is conducted from the body to the wooden tray. Hence, there is only a negligible drop in the temperature of the body and one does not feel cool.
Thus, a brass tumbler feels colder than a wooden tray on a chilly day.
Solution 2
Brass is a good conductor of heat, while wood is a bad conductor. When we touch the brass tumbler on a chilly day, heat starts flowing from our body to the tumbler and we feel it cold. However, when the wooden tray is touched, heat does not flow from our hands to the tray and we do not feel cold.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
A tightly closed metal lid of a glass bottle can be opened more easily if it is put in hot water for some time. Explain.
A steel frame (K = 45 W m−1°C−1) of total length 60 cm and cross sectional area 0.20 cm2, forms three sides of a square. The free ends are maintained at 20°C and 40°C. Find the rate of heat flow through a cross section of the frame.
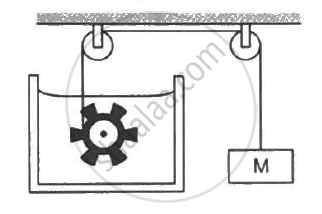
Following Figure shows water in a container having 2.0 mm thick walls made of a material of thermal conductivity 0.50 W m−1°C−1. The container is kept in a melting-ice bath at 0°C. The total surface area in contact with water is 0.05 m2. A wheel is clamped inside the water and is coupled to a block of mass M as shown in the figure. As the block goes down, the wheel rotates. It is found that after some time a steady state is reached in which the block goes down with a constant speed of 10 cm s−1 and the temperature of the water remains constant at 1.0°C. Find the mass M of the block. Assume that the heat flows out of the water only through the walls in contact. Take g = 10 m s−2.
On a winter day when the atmospheric temperature drops to −10°C, ice forms on the surface of a lake. (a) Calculate the rate of increase of thickness of the ice when 10 cm of the ice is already formed. (b) Calculate the total time taken in forming 10 cm of ice. Assume that the temperature of the entire water reaches 0°C before the ice starts forming. Density of water = 1000 kg m−3, latent heat of fusion of ice = 3.36 × 105 J kg−1and thermal conductivity of ice = 1.7 W m−1°C−1. Neglect the expansion of water of freezing.
A semicircular rod is joined at its end to a straight rod of the same material and the same cross-sectional area. The straight rod forms a diameter of the other rod. The junctions are maintained at different temperatures. Find the ratio of the heat transferred through a cross section of the semicircular rod to the heat transferred through a cross section of the straight rod in a given time.
A room has a window fitted with a single 1.0 m × 2.0 m glass of thickness 2 mm. (a) Calculate the rate of heat flow through the closed window when the temperature inside the room is 32°C and the outside is 40°C. (b) The glass is now replaced by two glasspanes, each having a thickness of 1 mm and separated by a distance of 1 mm. Calculate the rate of heat flow under the same conditions of temperature. Thermal conductivity of window glass = 1.0 J s−1 m−1°C−1 and that of air = 0.025 m-1°C-1 .
These days people use steel utensils with copper bottom. This is supposed to be good for uniform heating of food. Explain this effect using the fact that copper is the better conductor.
A thin rod having length L0 at 0°C and coefficient of linear expansion α has its two ends maintained at temperatures θ1 and θ2, respectively. Find its new length.
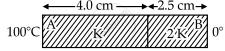
As per the given figure, two plates A and B of thermal conductivity K and 2 K are joined together to form a compound plate. The thickness of plates are 4.0 cm and 2.5 cm respectively and the area of cross-section is 120 cm2 for each plate. The equivalent thermal conductivity of the compound plate is `(1+5/alpha)`K, then the value of a will be ______.
A cylinder of radius R made of material of thermal conductivity K1 is surrounded by a cylindrical shell of inner radius R and outer radius 3R made of a material of thermal conductivity K2. The two ends of the combined system are maintained at two different temperatures. What is the effective thermal conductivity of the system?
