Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain why the p.d across the terminals of a cell is more in an open circuit and reduced in a closed circuit.
Solution
There is no drain on the cell's current when the circuit is open. Thus, the p.d. gradually evolved between the cell's electrodes due to chemical reactions within the cell. However, if a cell's current is removed, the voltage drops because the process of transferring a unit charge around the circuit formed by the cell's terminals requires energy. Therefore, in an open circuit, the potential difference across the cell's terminals is greater than in a closed circuit.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What happens to the resistivity of semiconductor with the increase of temperature?
Name two factors on which the internal resistance of a cell depends and state how does it depend on the factors stated by you.
A cell of e.m.f ε and internal resistance r is used to send current to an external resistance R. Write expressions for
- the total resistance of circuit.
- the current drawn from the cell.
- the p.d. across the cell.
- voltage drop inside the cell.
A cell is used to send current to an external circuit.
- How does the voltage across its terminals compare with its e.m.f.?
- Under what condition is the e.m.f. of a cell equal to its terminal voltage?
A battery of e.m.f 3.0 V supplies current through a circuit in which the resistance can be changed.
A high resistance voltmeter is connected across the battery. When the current is 1.5 A, the voltmeter reads 2.7 V. Find the internal resistance of the battery.
A cell of e.m.f. 2 V and internal resistance 1.2 Ω is connected to an ammeter of resistance 0.8 Ω and two resistors of 4.5 Ω and 9 Ω as shown in following figure.

Find:
- The reading of the ammeter,
- The potential difference across the terminals of the cells, and
- The potential difference across the 4.5 Ω resistor.
Four cells, each of e.m.f. 1.5 V and internal resistance 2.0 ohms are connected in parallel. The battery of cells is connected to an external resistance of 2.5 ohms. Calculate:
(i) The total resistance of the circuit.
(ii) The current flowing in the external circuit.
(iii) The drop in potential across-the terminals of the cells.
(a) Calculate the total resistance across AB.
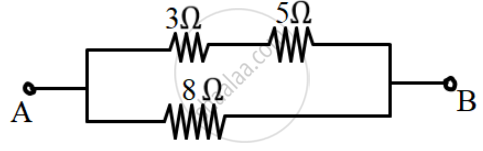
(b) If a cell of e.m.f 2.4 V with negligible internal resistance is connected across AB then calculate the current drawn from the cell.
Study the diagram:
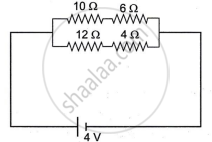
- Calculate the total resistance of the circuit.
- Calculate the current drawn from the cell.
- State whether the current through 10 Ω resistor is greater than, less than or equal to the current through the 12 Ω resistor.
A battery of e.m.f. 6·0 V supplies current through a circuit in which the resistance can be changed. A high resistance voltmeter is connected across the battery. When the current is 3 A, the voltmeter reads 5.4 V. Find the internal resistance of the battery.
