Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Explain, why the potential difference across the terminals of a cell is more when the cell is not in use than it is when the cell is being used.
Solution
The reason is that when the cell is being used, there is a drop in potential across the internal resistance of the cell.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw the electrical symbols of the following components and state its use:
Ammeter.
One coulomb of charge flows through any cross-section of a conductor in 1 second. What is the current flowing through the conductor?
The circuit diagram given below shows the combination of three resistors R1, R2 and R3:

Find :
(i) total resistance of the circuit.
(ii) total current flowing in the circuit.
(iii) the potential difference across R1.
Using the circuit given below, state which of the following statement is correct?
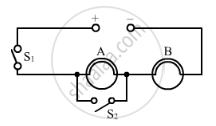
(a) When S1 and S2 are closed, lamps A and B are lit.22
(b) With S1 open and S2 closed, A is lit and B is not lit.
(c) With S2 open and S1 closed A and B are lit.
(d) With S1 closed and S2 open, lamp A remains lit even if lamp B gets fused.
State two differences between the e.m.f and terminal voltage of a cell.
Tick(✓) the correct choice in the following:
24 watt, 12 volt head lamp is fully lit by connecting it to a 12 volt
battery. The working resistance of the lamp is
If a fuse contains a 5 A fuse wire and the voltage is 240 V, what is the maximum power (wattage) which may be taken from the circuit?
An electric bulb is marked '100 W, 250 V'. What information does this convey?
Match the items in column-I to the items in column-II:
| Column - I | Column - II |
| (i) electric current | (a) volt |
| (ii) potential difference | (b) ohm meter |
| (iii) specific resistance | (c) watt |
| (iv) Electrical power | (d) joule |
| (v) electrical energy | (e) ampere |
