Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Find an odd one out.
Options
Stigma
Style
Pollens
Ovary
Solution
Pollens
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
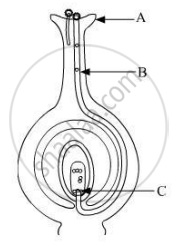
Name the parts A, B and C shown in the diagram and write their functions.
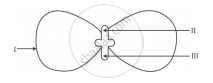
In the following diagram showing the structure of embryo of a dicot seed, what are the parts marked I, II and III sequentially?
Name the parts A, B and C shown in the following diagram and state one function of each.

A student has to perform the experiment "To identify the different parts of an embryo of a dicot seed." Select from the following an appropriate group of seeds:
(a) Pea, gram, wheat
(b) Red kidney bean, maize, gram
(c) Maize, wheat, red kidney bean
(d) Red kidney bean, pea, gram
Name and differentiate between the two modes of pollination in flowering plants.
Give one example of a unisexual flower.
Mention the changes a flower undergoes after fertilisation.
Name the swollen lower part of the carpel.
What is the function of a flower?
Where is the male gamete formed in flowering plants?
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The ovule becomes a .......... after fertilisation.
Fill in the following blank with suitable word :
The male organ of reproduction in the flower is the.......... .
Explain the terms 'self pollination'
How do the insects help in cross-pollination?
(a) Draw a neat diagram of a flower showing its various parts. In this diagram mark stem, receptacle, sepals, petals, stamen and carpel.
(b) What name is given to (i) all the petals of a flower, and (ii) all the sepals of a flower?
(c) What are (i) stamen, and (ii) carpel, in a flower?
(d) What is the other name of carpel of a flower?
(e) What is the name of yellow powdery substance present in the anther of a flower?
Which among the following statements are true for unisexual flowers?
(i) They possess both stamen and pistil
(ii) They possess either stamen or pistil
(iii) They exhibit cross pollination
(iv) Unisexual flower possessing only stamens cannot produce fruits
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii), (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (i), (iii) and (iv)
In what ways is fertilisation in a plant different from fertilisation in a human?
Fill in the blanks:
A stamen consists of ______ and ________.
Mention the function of Anther.
What are the male and female gametes in a flowering plant?
“Cell division is a type of reproduction in unicellular organism.” Justify.
Draw a diagram of a pistil showing pollen tube growth into the ovule and label the following:
Pollen grain, male gamete, female gamete, ovary.
Distinguish between unisexual and bisexual flowers giving one example of each. Draw a diagram showing process of germination of pollen grains on stigma and label the following parts:
(a) Female germ cell
(b) Male germ cell
(c) Ovary
Which of the following is not an unisexual flower?
a) Coconut
b) Papaya
c) Gulmohor
d) Maize
Sketch the labeled diagram:
Flower with its sexual reproductive organs
Write the functions of sepals
In which of the following manner the arrangement of megaspores in a tetrad is observed in angiosperms?
Sperm and egg nuclei fuse due to ______.
What would be the number of chromosomes in the cells of the aleurone layer in a plant species with 8 chromosomes in its synergids?
Is the chromosome number of zygote, embryonal cells and adult of a particular organism always constant? How is the constancy maintained in these three stages?
Where is the zygote located in the flower after fertilization?
The ovaries of different flowers may contain
Double fertilization means ______.
Triple fusion involves ______.
Sexual maturation of reproductive tissues and organs are necessary link for reproduction. Elucidate.
Name the reproductive parts of an angiosperm. Where are these parts located? Explain the structure of its male reproductive part.
The pollen tube usually enters the embryo sac ______.
