Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Frenkel defect is also known as:
(i) stoichiometric defect
(ii) dislocation defect
(iii) impurity defect
(iv) non-stoichiometric defect
Solution
(i) stoichiometric defect
(ii) dislocation defect
Explanation:
In Frenkel defect, dislocation of cations takes place and there is no change in stoichiometry of the crystal.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Examine the given defective crystal:

Answer the following questions :
(i) What type of stoichiometric defect is shown by the crystal?
(ii) How is the density of the crystal affected by this defect?
(iii) What type of ionic substances show such defect?
Out of NaCl and AgCl, which one shows Frenkel defect and why?
The radius of Cs+ is 169 pm and Cl− is 181 pm. The radius ratio is ____________.
Type of stoichiometric defect shown by ZnS is ____________.
The following diagram shows:
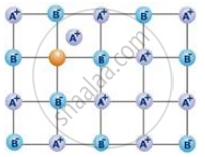
Alkali halids do not show Frenkel defect because ____________.
Cations are present in the interstitial sites in ______.
Match the defects given in Column I with the statements in given Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Simple vacancy defect | (a) shown by non-ionic solids and increases density of the solid. |
| (ii) Simple interstitial defect | (b) shown by ionic solids and decreases density of the solid. |
| (iii) Frenkel defect | (c) shown by non ionic solids and density of the solid decreases. |
| (iv) Schottky defect | (d) shown by ionic solids and density of the solid remains the same. |
Given below are two statements, one is labelled as Assertion (A) and the other is labelled as Reason (R):
Assertion: In any ionic solid (MX) with Schottky defects, the number of positive and negative ions are same.
Reason: Equal number of cation and anion vacancies are present.
If NaCl is doped with 10–4 mole percent of SrCl2 the concentration of cation vacancies will be
