Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Solutions
3: Electrochemistry
4: Chemical Kinetics
5: Surface Chemistry
6: General Principle and Processes of Isolation of Elements
7: The p-block Elements
8: The d-and f-Block Elements
9: Coordination Compounds
10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
13: Amines
14: Biomolecules
15: Polymers
16: Chemistry In Everyday Life
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 1 - Solid States NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 1 - Solid States - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 1: Solid States
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 1 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Chemistry [English] Class 12.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 1 Solid States Exercises [Pages 1 - 13]
Multiple Choice Questions (Type - I)
Which of the following conditions favours the existence of a substance in the solid state?
High temperature
Low temperature
High thermal energy
Weak cohesive forces
Which of the following is not a characteristic of a crystalline solid?
Definite and characteristic heat of fusion.
Isotropic nature.
A regular periodically repeated pattern of arrangement of constituent particles in the entire crystal.
A true solid.
A regular arrangement of constituent particles.
Sharp melting point.
Which of the following is an amorphous solid?
Graphite (C)
Quartz glass (SiO2)
Chrome alum
Silicon carbide (SiC)
Which of the following arrangements shows schematic alignment of magnetic moments of antiferromagnetic substances?
Which of the following is true about the value of refractive index of quartz glass?
Same in all directions
Different in different directions
Cannot be measured
Always zero
Which of the following statement is not true about amorphous solids?
On heating they may become crystalline at certain temperature.
They may become crystalline on keeping for long time.
Amorphous solids can be moulded by heating.
They are anisotropic in nature.
The sharp melting point of crystalline solids is due to ______.
a regular arrangement of constituent particles observed over a short distance in the crystal lattice
a regular arrangement of constituent particles observed over a long distance in the crystal lattice
same arrangement of constituent particles in different directions
different arrangement of constituent particles in different directions
Iodine molecules are held in the crystals lattice by ______.
london forces
dipole-dipole interactions
covalent bonds
coulombic forces
Which of the following is a network solid?
\[\ce{SO2}\] (Solid)
\[\ce{I2}\]
Diamond
\[\ce{H2O}\] (Ice)
Which of the following solids is not an electrical conductor?
- Mg (s)
- TiO (s)
- I2 (s)
- H2O (s)
Mg (s) only
TiO (s) only
I2 (s) and H2O (s)
TiO (s), I2 (s) and H2O (s)
Which of the following is not the characteristic of ionic solids?
Very low value of electrical conductivity in the molten state.
Brittle nature
Very strong forces of interactions.
Anisotropic nature
Graphite is a good conductor of electricity due to the presence of ______.
lone pair of electrons
free valence electrons
cations
anions
Which of the following oxides behaves as conductor or insulator depending upon temperature?
TiO
SiO2
TiO3
MgO
Which of the following oxides shows electrical properties like metals?
SiO2
MgO
SO2 (s)
CrO2
The lattice site in a pure crystal cannot be occupied by ______.
molecule
ion
electron
atom
Graphite cannot be classified as ______.
conducting solid
network solid
covalent solid
ionic solid
Cations are present in the interstitial sites in ______.
Frenkel defect
Schottky defect
Vacancy defect
Metal deficiency defect
Schottky defect is observed in crystals when ______.
some cations move from their lattice site to interstitial sites.
equal number of cations and anions are missing from the lattice.
some lattice sites are occupied by electrons.
some impurity is present in the lattice.
Which of the following is true about the charge acquired by p-type semiconductors?
Positive
Neutral
Negative
Depends on concentration of p impurity
To get a n-type semiconductor from silicon, it should be doped with a substance with valence ______.
2
1
3
5
The total number of tetrahedral voids in the face-centered unit cell is ______.
6
8
10
12
Which of the following point defects are shown by AgBr(s) crystals?
- Schottky defect
- Frenkel defect
- Metal excess defect
- Metal deficiency defect
A and B
C and D
A and C
B and D
In which pair is most efficient packing is present?
hcp and bcc
hcp and ccp
bcc and ccp
bcc and simple cubic cell
The percentage of empty space in a body centred cubic arrangement is ______.
74
68
32
26
Which of the following statement is not true about the hexagonal close packing?
The coordination number is 12.
It has 74% packing efficiency.
Tetrahedral voids of the second layer are covered by the spheres of the third layer.
In this arrangement spheres of the fourth layer are exactly aligned with those of the first layer.
In which of the following structures coordination number for cations and anions in the packed structure will be same?
Cl– ion form fcc lattice and Na+ ions occupy all octahedral voids of the unit cell.
Ca2+ ions form fcc lattice and F– ions occupy all the eight tetrahedral voids of the unit cell.
O2– ions form fcc lattice and Na+ ions occupy all the eight tetrahedral voids of the unit cell.
S2– ions form fcc lattice and Zn2+ ions go into alternate tetrahedral voids of the unit cell.
What is the coordination number in a square close packed structure in two dimensions?
2
3
4
6
Which kind of defects are introduced by doping?
Dislocation defect
Schottky defect
Frenkel defects
Electronic defects
Silicon doped with electron-rich impurity forms ______.
p-type semiconductor
n-type semiconductor
intrinsic semiconductor
insulator
Which of the following statements is not true?
Paramagnetic substances are weakly attracted by magnetic field.
Ferromagnetic substances cannot be magnetised permanently.
The domains in antiferromagnetic substances are oppositely oriented with respect to each other.
Pairing of electrons cancels their magnetic moment in the diamagnetic substances.
Which of the following is not true about the ionic solids?
Bigger ions form the close packed structure.
Smaller ions occupy either the tetrahedral or the octahedral voids depending upon their size.
Occupation of all the voids is not necessary.
The fraction of octahedral or tetrahedral voids occupied depends upon the radii of the ions occupying the voids.
A ferromagnetic substance becomes a permanent magnet when it is placed in a magnetic field becuase ______.
all the domains get oriented in the direction of magnetic field.
all the domains get oriented in the direction opposite to the direction of magnetic field.
domains get oriented randomly.
domains are not affected by magnetic field.
The correct order of the packing efficiency in different types of unit cells is ______.
fcc < bcc < simple cubic
fcc > bcc > simple cubic
fcc < bcc > simple cubic
bcc < fcc > simple cubi
Which of the following defects is also known as dislocation defect?
Frenkel defect
Schottky defect
Non-stoichiometric defect
Simple interstitial defect
In the cubic close packing, the unit cell has ______.
4 tetrahedral voids each of which is shared by four adjacent unit cells.
4 tetrahedral voids within the unit cell.
8 tetrahedral voids each of the which is shared by four adjacent unit cells.
8 tetrahedral voids within the unit cells.
The edge lengths of the unit cells in terms of the radius of spheres constituting fcc, bcc and simple cubic unit cell are respectively ______.
`2sqrt(2)r, (4r)/sqrt(3), 2r`
`(4r)/sqrt(3), 2sqrt(2)r, 2r`
`2r, 2sqrt(2)r, (4r)/sqrt(3)`
`2r, (4r)/sqrt(3), 2sqrt(2)r`
Which of the following represents correct order of conductivity in solids?
\[\ce{Κ_{metal} >> K_{insulators} < K_{semiconductors}}\]
\[\ce{Κ_{metal} << K_{insulators} < K_{semiconductors}}\]
\[\ce{Κ_{metal} ≅ K_{insulators} > K_{semiconductors} = zero}\]
\[\ce{Κ_{metal} < K_{insulators} > K_{semiconductors} ≠ zero}\]
Multiple Choice Questions (Type - II) Note: In the following questions two or more options may be correct.
Which of the following is not true about the voids formed in 3 dimensional hexagonal close packed structure?
(i) A tetrahedral void is formed when a sphere of the second layer is present above triangular void in the first layer.
(ii) All the triangular voids are not covered by the spheres of the second layer.
(iii) Tetrahedral voids are formed when the triangular voids in the second layer lie above the triangular voids in the first layer and the triangular shapes of these voids do not overlap.
(iv) Octahedral voids are formed when the triangular voids in the second layer exactly overlap with similar voids in the first layer.
The value of magnetic moment is zero in the case of antiferromagnetic substances because the domains:
(i) get oriented in the direction of the applied magnetic field.
(ii) get oriented opposite to the direction of the applied magnetic field.
(iii) are oppositely oriented with respect to each other without the application of magnetic field.
(iv) cancel out each other’s magnetic moment.
Which of the following statements are not true?
(i) Vacancy defect results in a decrease in the density of the substance.
(ii) Interstitial defects results in an increase in the density of the substance.
(iii) Impurity defect has no effect on the density of the substance.
(iv) Frankel defect results in an increase in the density of the substance.
Which of the following statements are true about metals?
(i) Valence band overlaps with conduction band.
(ii) The gap between valence band and conduction band is negligible.
(iii) The gap between valence band and conduction band cannot be determined.
(iv) Valence band may remain partially filled.
Under the influence of electric field, which of the following statements is true about the movement of electrons and holes in a p-type semiconductor?
(i) Electron will move towards the positvely charged plate through electron holes.
(ii) Holes will appear to be moving towards the negatively charged plate.
(iii) Both electrons and holes appear to move towards the positively charged plate.
(iv) Movement of electrons is not related to the movement of holes.
Which of the following statements are true about semiconductors?
(i) Silicon doped with electron-rich impurity is a p-type semiconductor.
(ii) Silicon doped with an electron-rich impurity is an n-type semiconductor.
(iii) Delocalised electrons increase the conductivity of doped silicon.
(iv) An electron vacancy increases the conductivity of n-type semiconductor.
An excess of potassium ions makes KCl crystals appear violet or lilac in colour since:
(i) some of the anionic sites are occupied by an unpaired electron.
(ii) some of the anionic sites are occupied by a pair of electrons.
(iii) there are vacancies at some anionic sites.
(iv) F-centres are created which impart colour to the crystals.
The number of tetrahedral voids per unit cell in NaCl crystal is:
(i) 4
(ii) 8
(iii) twice the number of octahedral voids.
(iv) four times the number of octahedral voids.
Amorphous solid can also be called:
(i) pseudo solids
(ii) true solids
(iii) supercooled liquids
(iv) supercooled solids
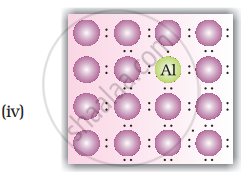
A perfect crystal of silicon (Figure) is doped with some elements as given in the options. Which of these options show n-type semiconductors?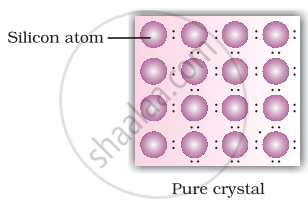
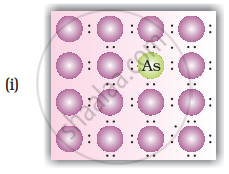
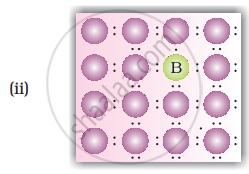
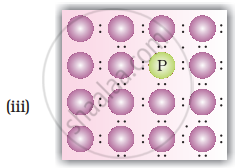
Which of the following statements are correct?
(i) Ferrimagnetic substances lose ferrimagnetism on heating and become paramagnetic.
(ii) Ferrimagnetic substances do not lose ferrimagnetism on heating and remain ferrimagnetic.
(iii) Antiferromagnetic substances have domain structures similar to ferromagnetic substances and their magnetic moments are not cancelled by each other.
(iv) In ferromagnetic substances all the domains get oriented in the direction of magnetic field and remain as such even after removing magnetic field.
Which of the following features are not shown by quartz glass?
(i) This is a crystalline solid.
(ii) Refractive index is same in all the directions.
(iii) This has definite heat of fusion.
(iv) This is also called super cooled liquid.
Which of the following cannot be regarded as molecular solid?
(i) SiC (Silicon carbide)
(ii) AlN
(iii) Diamond
(iv) I2
In which of the following arrangements octahedral voids are formed?
(i) hcp
(ii) bcc
(iii) simple cubic
(iv) fcc
Frenkel defect is also known as:
(i) stoichiometric defect
(ii) dislocation defect
(iii) impurity defect
(iv) non-stoichiometric defect
Which of the following defects decrease the density?
(i) Interstitial defect
(ii) Vacancy defect
(iii) Frankel defect
(iv) Schottky defect
III. Short Answer Type
Why are liquids and gases categorised as fluids?
Why are solids incompressible?
Inspite of long range order in the arrangement of particles why are the crystals usually not perfect?
Why does table salt, NaCl, some times appear yellow in colour?
Why is FeO (s) not formed in stoichiometric composition?
Why does white ZnO (s) becomes yellow upon heating?
Why does the electrical conductivity of semiconductors increase with rise in temperature?
Explain why does conductivity of germanium crystals increase on doping with galium.
In a compound, nitrogen atoms (N) make cubic close packed lattice and metal atoms (M) occupy one-third of the tetrahedral voids present. Determine the formula of the compound formed by M and N?
Under which situations can an amorphous substance change to crystalline form?
Matching Type Note: In the following questions match the items given in Column I with the items given in Column II. In some questions more than one item of Column I and Column II may match.
Match the defects given in Column I with the statements in given Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Simple vacancy defect | (a) shown by non-ionic solids and increases density of the solid. |
| (ii) Simple interstitial defect | (b) shown by ionic solids and decreases density of the solid. |
| (iii) Frenkel defect | (c) shown by non ionic solids and density of the solid decreases. |
| (iv) Schottky defect | (d) shown by ionic solids and density of the solid remains the same. |
Match the type of unit cell given in Column I with the features given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Primitive cubic unit cell | (a) Each of the three perpendicular edges compulsorily have the different edge length i.e; a ≠ b ≠ c. |
| (ii) Body centred cubic unit cell | (b) Number of atoms per unit cell is one. |
| (iii) Face centred cubic unit cell | (c) Each of the three perpendicular edges compulsorily have the same edge length i.e; a = b = c. |
| (iv) End centred orthorhombic cell | (d) In addition to the contribution from unit cell the corner atoms the number of atoms present in a unit cell is one. |
| (e) In addition to the contribution from the corner atoms the number of atoms present in a unit cell is three. |
Match the types of defect given in Column I with the statement given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Impurity defect | (a) NaCl with anionic sites called F-centres |
| (ii) Metal excess defect | (b) FeO with Fe3+ |
| (iii) Metal deficiency defect | (c) NaCl with Sr2+ and some cationic sites vacant |
Match the items given in Column I with the items given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Mg in solid state | (a) p-Type semiconductor |
| (ii) MgCl2 in molten state | (b) n-Type semiconductor |
| (iii) Silicon with phosphorus | (c) Electrolytic conductors |
| (iv) Germanium with boron | (d) Electronic conductors |
Match the type of packing given in Column I with the items given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II |
| (i) Square close packing in two dimensions |
(a) Triangular voids |
| (ii) Hexagonal close packing in two dimensions |
(b) Pattern of spheres is repeated in every fourth layer |
| (iii) Hexagonal close packing in three dimensions |
(c) Coordination number 4 |
| (iv) Cubic close packing in three dimensions |
(d) Pattern of sphere is repeated in alternate layers |
Assertion and Reason Type Note: In the following questions a statement of assertion followed by a statement of reason is given. Choose the correct answer out of the following choices.
Assertion: The total number of atoms present in a simple cubic unit cell is one.
Reason: Simple cubic unit cell has atoms at its corners, each of which is shared between eight adjacent unit cells.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion: Graphite is a good conductor of electricity however diamond belongs to the category of insulators.
Reason: Graphite is soft in nature on the other hand diamond is very hard and brittle.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion: Total number of octahedral voids present in unit cell of cubic close packing including the one that is present at the body centre, is four.
Reason: Besides the body centre there is one octahedral void present at the centre of each of the six faces of the unit cell and each of which is shared between two adjacent unit cells.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion: The packing efficiency is maximum for the fcc structure.
Reason: The cordination number is 12 in fcc structures.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Assertion: Semiconductors are solids with conductivities in the intermediate range from 10–6 – 104 ohm–1m–1.
Reason: Intermediate conductivity in semiconductor is due to partially filled valence band.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason is correct explanation for assertion.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation for assertion.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Long Answer Type
With the help of a labelled diagram show that there are four octahedral voids per unit cell in a cubic close packed structure.
Show that in a cubic close packed structure, eight tetrahedral voids are present per unit cell.
How does the doping increase the conductivity of semiconductors?
A sample of ferrous oxide has actual formula Fe0.93O1.00. In this sample what fraction of metal ions are Fe2+ ions? What type of nonstoichiometric defect is present in this sample?
Solutions for 1: Solid States
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 1 - Solid States NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 1 - Solid States - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 1 - Solid States
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE 1 (Solid States) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 1 Solid States are Classification of Crystalline Solids, Amorphous and Crystalline Solids, Crystal Lattices and Unit Cells, Calculations Involving Unit Cell Dimensions, Close Packed Structures of Solids, Efficiency of Packing in Body-centred Cubic Structures, Close Packed Structures - Formula of a Compound and Number of Voids Filled, Number of Atoms in a Unit Cell, Imperfections in Solids - Introduction, Magnetic Properties, Band Theory of Metals, Electrical Properties - Introduction, Applications of n-type and p-type Semiconductors, General Characteristics of Solid State, Crystal Lattices and Unit Cells - Primitive and Centred Unit Cells, Packing Efficiency in hcp and ccp Structures, Packing Efficiency in Simple Cubic Lattice, Types of Point Defects - Stoichiometric Defects, Types of Point Defects - Impurity Defects, Types of Point Defects - Non-stoichiometric Defects, Conduction of Electricity in Metals, Conduction of Electricity in Semiconductors, Solid State Numericals.
Using NCERT Exemplar Chemistry [English] Class 12 solutions Solid States exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Chemistry [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 1, Solid States Chemistry [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.




