Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Solutions
3: Electrochemistry
4: Chemical Kinetics
5: Surface Chemistry
6: General Principle and Processes of Isolation of Elements
7: The p-block Elements
8: The d-and f-Block Elements
9: Coordination Compounds
10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
▶ 11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
13: Amines
14: Biomolecules
15: Polymers
16: Chemistry In Everyday Life
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 11 - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 11 - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 11 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Chemistry [English] Class 12.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Multiple Choice Questions (Type - I) [Pages 154 - 164]
Monochlorination of toluene in sunlight followed by hydrolysis by aq. \[\ce{NaOH}\] yields.
o-Cresol
m-Cresol
2, 4-Dihydroxytoluene
Benzyl alcohol
How many alcohol(s) with molecular formula \[\ce{C4H10O}\] is chiral in nature?
1
2
3
4
What is the correct order of reactivity of alcohols in the following reaction?
\[\ce{R-OH + HCl ->[ZnCl2] R-Cl + H2O}\]
1° > 2° > 3°
1° < 2° > 3°
3° > 2° > 1°
3° > 1° > 2°
\[\ce{CH3CH2OH}\] can be converted into \[\ce{CH3CHO}\] by ______.
catalytic hydrogenation
treatment with \[\ce{LiAlH4}\]
treatment with pyridinium chlorochromate
treatment with \[\ce{KMnO4}\]
The process of converting alkyl halides into alcohols involves ______.
addition reaction
substitution reaction
dehydrohalogenation reaction
rearrangement reaction
Which of the following compounds is aromatic alcohol?
| (A) |  |
| (B) | 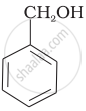 |
| (C) | 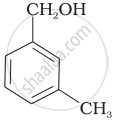 |
| (D) | 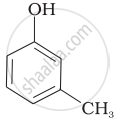 |
A, B, C, D
A, D
B, C
A
Give IUPAC name of the compound given below.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - CH - CH2 - CH2 - CH - CH3}\phantom{.}\\
\phantom{.........}|\phantom{...................}|\phantom{...........}\\
\phantom{..}\ce{Cl}\phantom{.................}\ce{OH}\phantom{..}
\end{array}\]
2-Chloro-5-hydroxyhexane
2-Hydroxy-5-chlorohexane
5-Chlorohexan-2-ol
2-Chlorohexan-5-ol
IUPAC name of m-cresol is ______.
3-methylphenol
3-chlorophenol
3-methoxyphenol
benzene-1,3-diol
IUPAC name of the compound \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH - OCH3}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{....}\\
\phantom{}\ce{CH3}\phantom{..}
\end{array}\] is ______.
1-methoxy-1-methylethane
2-methoxy-2-methylethane
2-methoxypropane
isopropylmethyl ether
Which of the following species can act as the strongest base?
ΘOH
ΘOR
ΘOC6H5
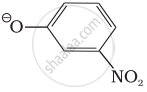
Which of the following compounds will react with sodium hydroxide solution in water?
\[\ce{C6H5OH}\]
\[\ce{C6H5CH2OH}\]
\[\ce{(CH3)3COH}\]
\[\ce{C2H5OH}\]
Phenol is less acidic than ______.
ethanol
o-nitrophenol
o-methylphenol
o-methoxyphenol
Which of the following is most acidic?
Benzyl alcohol
Cyclohexanol
Phenol
m-Chlorophenol
Mark the correct order of decreasing acid strength of the following compounds.
| (a) | 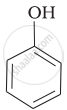 |
| (b) | 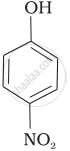 |
| (c) | 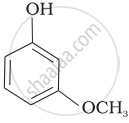 |
| (d) | 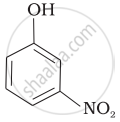 |
| (e) | 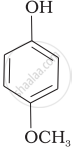 |
e > d > b > a > c
b > d > a > c > e
d > e > c > b > a
e > d > c > b > a
Mark the correct increasing order of reactivity of the following compounds with HBr/HCl.
| (a) | 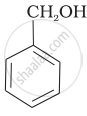 |
| (b) | 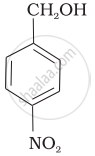 |
| (c) | 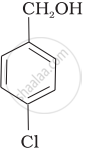 |
a < b < c
b < a < c
b < c < a
c < b < a
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of boiling point. Propan-1-ol, butan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, pentan-1-ol
Propan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, butan-1-ol, pentan-1-ol
Propan-1-ol, butan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, pentan-1-ol
Pentan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, butan-1-ol, propan-1-ol
Pentan-1-ol, butan-1-ol, butan-2-ol, propan-1-ol
Which of the following are used to convert \[\ce{RCHO}\] into \[\ce{RCH2OH}\]?
(i) \[\ce{H2/Pd}\]
(ii) \[\ce{LiAlH4}\]
(iii) \[\ce{NaBH4}\]
(iv) Reaction with \[\ce{RMgX}\] followed by hydrolysis
Which of the following reactions will yield phenol?
| (i) | 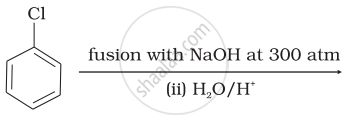 |
| (ii) | 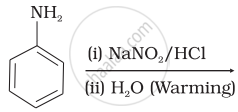 |
| (iii) | 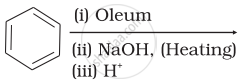 |
| (iv) | 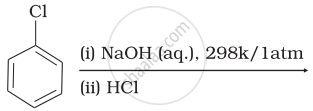 |
Which of the following reagents can be used to oxidise primary alcohols to aldehydes?
(i) \[\ce{CrO3}\] in anhydrous medium.
(ii) \[\ce{KMnO4}\] in acidic medium.
(iii) Pyridinium chlorochromate.
(iv) Heat in the presence of Cu at 573 K.
Phenol can be distinguished from ethanol by the reactions with:
(i) \[\ce{Br2/water}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Na}\]
(iii) Neutral \[\ce{FeCl3}\]
(iv) All the above
Which of the following are benzylic alcohols?
(i) \[\ce{C6H5 - CH2 - CH2OH}\]
(ii) \[\ce{C6H5 - CH2OH}\]
(iii) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{C6H5 - CH - OH}\\
\phantom{}|\phantom{.}\\
\phantom{..}\ce{CH3}\phantom{}
\end{array}\]
(iv) \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{C6H5 - CH2 - CH - OH}\\
\phantom{.......}|\phantom{}\\
\phantom{.........}\ce{CH3}\phantom{}
\end{array}\]
What is the structure and IUPAC name of glycerol?
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{.}\ce{CH3 - CH - CH - CH - CH - CH3}\phantom{}\\
\phantom{......}|\phantom{......}|\phantom{......}|\phantom{.....}|\phantom{........}\\
\phantom{...}\ce{CH3}\phantom{...}\ce{OH}\phantom{...}\ce{C2H5}\phantom{.}\ce{OH}\phantom{...}\end{array}\]
Write the IUPAC name of the following compound.
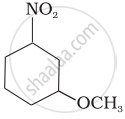
Write the IUPAC name of the compound given below.
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{}\ce{CH3 - CH2 - C = C - OH}\\
\phantom{........}|\phantom{....}|\phantom{}\\
\phantom{..............}\ce{CH3 CH2OH}
\end{array}\]
Name the factors responsible for the solubility of alcohols in water.
What is denatured alcohol?
Suggest a reagent for the following conversion.

Out of 2-chloroethanol and ethanol which is more acidic and why?
Suggest a reagent for conversion of ethanol to ethanal.
Suggest a reagent for conversion of ethanol to ethanoic acid.
Out of o-nitrophenol and p-nitrophenol, which is more volatile? Explain.
Out of o-nitrophenol and o-cresol which is more acidic?
When phenol is treated with bromine water, white precipitate is obtained. Give the structure and the name of the compound formed.
Arrange the following compounds in increasing order of acidity and give a suitable explanation.
Phenol, o-nitrophenol, o-cresol
Alcohols react with active metals e.g. Na, K etc. to give corresponding alkoxides. Write down the decreasing order of reactivity of sodium metal towards primary, secondary and tertiary alcohols.
What happens when benzene diazonium chloride is heated with water?
Arrange the following compounds in decreasing order of acidity.
\[\ce{H2O, ROH, HC ≡ CH}\]
Name the enzymes and write the reactions involved in the preparation of ethanol from sucrose by fermentation.
How can propan-2-one be converted into tert- butyl alcohol?
Write the structures of the isomers of alcohols with molecular formula \[\ce{C4H10O}\]. Which of these exhibits optical activity?
Explain why is OH group in phenols more strongly held as compared to OH group in alcohols.
Explain why nucleophilic substitution reactions are not very common in phenols.
Preparation of alcohols from alkenes involves the electrophilic attack on alkene carbon atom. Explain its mechanism.
Explain why is \[\ce{O = C =O}\] nonpolar while \[\ce{R - O - R}\] is polar.
Why is the reactivity of all the three classes of alcohols with conc. \[\ce{HCl}\] and \[\ce{ZnCl2}\] (Lucas reagent) different?
Write steps to carry out the conversion of phenol to aspirin.
Nitration is an example of aromatic electrophilic substitution and its rate depends upon the group already present in the benzene ring. Out of benzene and phenol, which one is more easily nitrated and why?
In Kolbe’s reaction, instead of phenol, phenoxide ion is treated with carbon dioxide. Why?
Dipole moment of phenol is smaller than that of methanol. Why?
Ethers can be prepared by Williamson synthesis in which an alkyl halide is reacted with sodium alkoxide. Di-tert-butyl ether can’t be prepared by this method. Explain.
Why is the C – O – H bond angle in alcohols slightly less than the tetrahedral angle whereas the C – O – C bond angle in ether is slightly greater?
Explain why low molecular mass alcohols are soluble in water.
Explain why p-nitrophenol is more acidic than phenol.
Explain why alcohols and ethers of comparable molecular mass have different boiling points?
The carbon-oxygen bond in phenol is slightly stronger than that in methanol. Why?
Arrange water, ethanol and phenol in increasing order of acidity and give reason for your answer.
Match the structures of the compounds given in Column I with the name of the compounds given in Column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) | 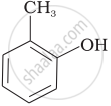 |
(a) Hydroquinone |
| (ii) | 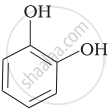 |
(b) Phenetole |
| (iii) | 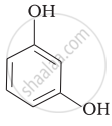 |
(c) Catechol |
| (iv) | 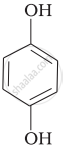 |
(d) o-Cresol |
| (v) | 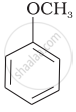 |
(e) guinone |
| (vi) | 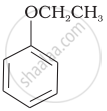 |
(f) Resorcinol |
| (g) Anisole |
Match the starting materials given in Column I with the products formed by these (Column II) in the reaction with HI.
| Column I | Column II | ||
| (i) | CH3—O—CH3 | (a) | 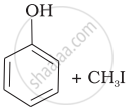 |
| (ii) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{..................}\\ \backslash\phantom{.............}\\ \ce{CH-O-CH3}\\ /\phantom{..............}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{..................} \end{array}\] |
(b) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{....}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3-C-I + CH3OH}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{....} \end{array}\] |
| (iii) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{.}\\ |\phantom{....}\\ \ce{H3C-C-O-CH3}\\ |\phantom{....}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{..} \end{array}\] |
(c) | 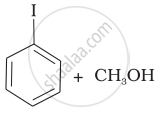 |
| (iv) | 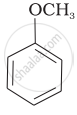 |
(d) | CH3—OH + CH3—I |
| (e) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................}\\ \backslash\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH-OH + CH3I}\\ /\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................} \end{array}\] |
||
| (f) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................}\\ \backslash\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH-I + CH3OH}\\ /\phantom{.................}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{.....................} \end{array}\] |
||
| (g) | \[\begin{array}{cc} \ce{CH3}\phantom{....}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3-C-OH + CH3I}\\ |\phantom{.......}\\ \ce{CH3}\phantom{....} \end{array}\] |
Match the items of column I with items of column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) | Antifreeze used in car engine | (a) Neutral ferric chloride |
| (ii) | Solvent used in perfumes | (b) Glycerol |
| (iii) | Starting material for picric acid | (c) Methanol |
| (iv) | Wood spirit | (d) Phenol |
| (v) | Reagent used for detection of phenolic group | (e) Ethleneglycol |
| (vi) | By product of soap industry used in cosmetics | (f) Ethanol |
Match the items of column I with items of column II.
| Column I | Column II | |
| (i) | Methanol | (a) Conversion of phenol to o-hydroxysalicylic acid |
| (ii) | Kolbe’s reaction | (b) Ethyl alcohol |
| (iii) | Williamson’s synthesis | (c) Conversion of phenol to salicylaldehyde |
| (iv) | Conversion of 2° alcohol to ketone | (d) Wood spirit |
| (v) | Reimer-Tiemann reaction | (e) Heated copper at 573 K |
| (vi) | Fermentation | (f) Reaction of alkyl halide with sodium alkoxide |
Assertion: Addition reaction of water to but-1-ene in acidic medium yields butan-1-ol.
Reason: Addition of water in acidic medium proceeds through the formation of primary carbocation.
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Both assertion and reason are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion: p-nitrophenol is more acidic than phenol.
Reason: Nitro group helps in the stabilisation of the phenoxide ion by dispersal of negative charge due to resonance.
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Both assertion and reason are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion: IUPAC name of the compound
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CH3 - CH - O - CH2 - CH2 - CH3}\\
|\phantom{....................}\\
\ce{CH3}\phantom{.................}
\end{array}\] is 2-Ethoxy-2-methylethane.
Reason: In IUPAC nomenclature, ether is regarded as hydrocarbon derivative in which a hydrogen atom is replaced by —OR or —OAr group [where R = alkyl group and Ar = aryl group]
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Both assertion and reason are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion: Bond angle in ethers is slightly less than the tetrahedral angle.
Reason: There is a repulsion between the two bulky (–R) groups.
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Both assertion and reason are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion: Boiling points of alcohols and ethers are high.
Reason: They can form intermolecular hydrogen-bonding.
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Both assertion and reason are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion: Like bromination of benzene, bromination of phenol is also carried out in the presence of Lewis acid.
Reason: Lewis acid polarises the bromine molecule.
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Both assertion and reason are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion: o-Nitrophenol is less soluble in water than the m- and p-isomers.
Reason: m- and p- Nitrophenols exist as associated molecules.
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Both assertion and reason are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion: Ethanol is a weaker acid than phenol.
Reason: Sodium ethoxide may be prepared by the reaction of ethanol with aqueous \[\ce{NaOH}\].
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Both assertion and reason are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion: Phenol forms 2, 4, 6 – tribromophenol on treatment with \[\ce{Br2}\] in carbon disulphide at 273 K.
Reason: Bromine polarises in carbon disulphide.
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Both assertion and reason are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion: Phenols give o- and p-nitrophenol on nitration with conc. \[\ce{HNO3}\] and \[\ce{H2SO4}\] mixture.
Reason: –OH group in phenol is o–, p– directing.
Assertion and reason both are correct and reason is correct explanation of assertion.
Assertion and reason both are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement but reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement but reason is correct statement.
Both assertion and reason are correct statements but reason is not correct explanation of assertion.
Write the mechanism of the reaction of HI with methoxymethane.
Name the starting material used in the industrial preparation of phenol.
Write complete reaction for the bromination of phenol in aqueous and non-aqueous medium.
Explain why Lewis acid is not required in bromination of phenol?
How can phenol be converted to aspirin?
Explain a process in which a biocatalyst is used in industrial preparation of a compound known to you.
Solutions for 11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 11 - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 11 - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 11 - Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE 11 (Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 11 Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers are Classification of Alcohols and Phenols, Nomenclature, Physical and Chemical Properties of Alcohols and Phenols, Preparation of Commercially Important Alcohols, Classification of Ethers, Structures of Functional Groups of Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers, Methods of Preparation of Alcohols, Methods of Preparation of Phenols, Reactions Involving Cleavage of O-H Bond, Reactions Involving Cleavage of Carbon–Oxygen (C–O) Bond in Alcohols, Chemical Properties of Phenol, Preparation of Ethers, Physical Properties of Ethers, Chemical Reaction of Ethers - Cleavege of C-O Bonds, Chemical Reaction of Ethers - Electrophilic Substitution.
Using NCERT Exemplar Chemistry [English] Class 12 solutions Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Chemistry [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 11, Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers Chemistry [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.
