Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Preparation of alcohols from alkenes involves the electrophilic attack on alkene carbon atom. Explain its mechanism.
Solution
The mechanism of the reaction involves the following three steps:
Step 1: Protonation of alkene to form carbocation by the electrophilic attack of H3O+.
\[\ce{H2O + H+ -> H3O+}\]
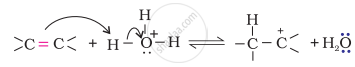
Step 2: Nucleophilic attack of water on carbocation.
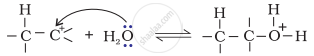
Step 3: Deprotonation to form an alcohol.
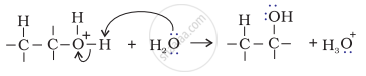
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Explain the mechanism of the following reaction:
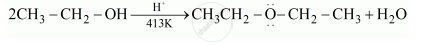
Account for the following :
t-butyl chloride on heating with sodium methoxide gives 2-methylpropene instead of t-butyl methyl ether.
The major product [B] in the following reactions is:
\[\begin{array}{cc}\ce{CH3}\phantom{..................................}\\|\phantom{.....................................}\\\ce{CH3 - CH2 - CH - CH2 - OCH2 - CH3 ->[HI][Heat] [A] alcohol ->[H2SO4][\Delta] [B]}\end{array}\]
Write the name of reagent and equation for the preparation of the following ether by Williamson’s synthesis:
2-Methoxy-2-methylpropane
Write the name of the reagent and equation for the preparation of the following ether by Williamson’s synthesis:
2-Methoxy-2-methylpropane
What is metamerism? Give the structure and IUPAC name of metamers of 2-methoxy propane.
Identify the product (s) is/are formed when 1-methoxy propane is heated with excess HI. Name the mechanism involved in the reaction.
Write the name of reagent and equation for the preparation of the following ethers by Williamson’s synthesis:
2-Methoxy-2-methylpropane
What will be the product (X and A)for the following reaction
\[\ce{acetylchloride->[i)CH3MgBr][ii)H3O+]X ->[acidk2crp3]A}\]
Give the structure and IUPAC name of metamers of 2-methoxy propane
