Advertisements
Online Mock Tests
Chapters
2: Solutions
3: Electrochemistry
4: Chemical Kinetics
5: Surface Chemistry
6: General Principle and Processes of Isolation of Elements
7: The p-block Elements
8: The d-and f-Block Elements
9: Coordination Compounds
10: Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
11: Alcohols, Phenols and Ethers
12: Aldehydes, Ketones and Carboxylic Acids
13: Amines
▶ 14: Biomolecules
15: Polymers
16: Chemistry In Everyday Life
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 14 - Biomolecules NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 14 - Biomolecules - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
Advertisements
Solutions for Chapter 14: Biomolecules
Below listed, you can find solutions for Chapter 14 of CBSE NCERT Exemplar for Chemistry [English] Class 12.
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 14 Biomolecules Multiple Choice Questions (Type - I) [Pages 202 - 213]
Glycogen is a branched-chain polymer of α-D-glucose units in which chain is formed by C1 – C4 glycosidic linkage whereas branching occurs by the formation of C1 – C6 glycosidic linkage. Structure of glycogen is similar to ______.
Amylose
Amylopectin
Cellulose
Glucose
Which of the following polymer is stored in the liver of animals?
Amylose
Cellulose
Amylopectin
Glycogen
Sucrose (cane sugar) is a disaccharide. One molecule of sucrose on hydrolysis gives ______.
2 molecules of glucose
2 molecules of glucose + 1 molecule of fructose
1 molecule of glucose + 1 molecule of fructose
2 molecules of fructose
Which of the following pairs represents anomers?
Proteins are found to have two different types of secondary structures viz. α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure. α-helix structure of protein is stabilised by:
Peptide bonds
van der Waals forces
Hydrogen bonds
Dipole-dipole interactions
In disaccharides, if the reducing groups of monosaccharides i.e. aldehydic or ketonic groups are bonded, these are non-reducing sugars. Which of the following disaccharide is a non-reducing sugar?
Which of the following acids is a vitamin?
Aspartic acid
Ascorbic acid
Adipic acid
Saccharic acid
Dinucleotide is obtained by joining two nucleotides together by phosphodiester linkage. Between which carbon atoms of pentose sugars of nucleotides are these linkages present?
5′ and 3'
1′ and 5′
5′ and 5′
3′ and 3′
Nucleic acids are the polymers of ______.
Nucleosides
Nucleotides
Bases
Sugars
Which of the following statements is not true about glucose?
It is an aldohexose.
On heating with HI it forms n-hexane.
It is present in furanose form.
It does not give 2,4-DNP test.
Each polypeptide in a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is said to be ______.
Primary structure of proteins
Secondary structure of proteins
Tertiary structure of proteins
Quaternary structure of proteins
DNA and RNA contain four bases each. Which of the following bases is not present in RNA?
Adenine
Uracil
Thymine
Cytosine
Which of the following B group vitamins can be stored in our body?
Vitamin B1
Vitamin B2
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B12
Which of the following bases is not present in DNA?
Adenine
Thymine
Cytosine
Uracil
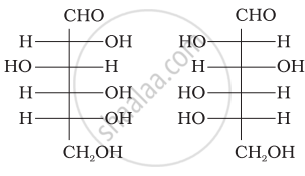
Three cyclic structures of monosaccharides are given below which of these are anomers.
| (I) | 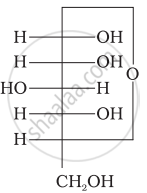 |
| (II) | 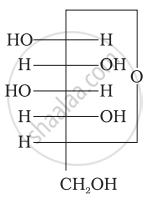 |
| (III) | 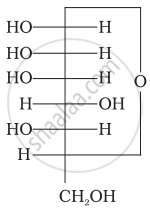 |
I and II
II and III
I and III
III is anomer of I and II
Which of the following reactions of glucose can be explained only by its cyclic structure?
Glucose forms pentaacetate
Glucose reacts with hydroxylamine to form an oxime
Pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine
Glucose is oxidised by nitric acid to gluconic acid
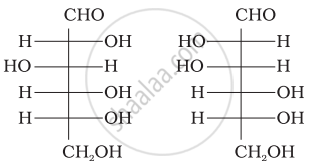
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
| (I) | 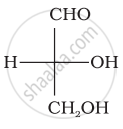 |
| (II) | 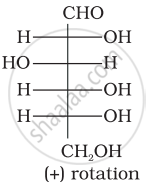 |
| (III) | 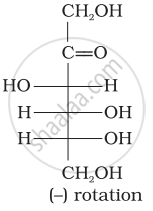 |
I, II, III
II, III
I, II
III
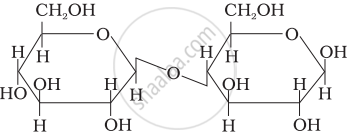
Structure of a disaccharide formed by glucose and fructose is given below. Identify anomeric carbon atoms in monosaccharide units.

‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘a’ carbon of fructose.
‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘e’ carbon of fructose.
‘a’ carbon of glucose and ‘b’ carbon of fructose.
‘f’ carbon of glucose and ‘f ’ carbon of fructose.
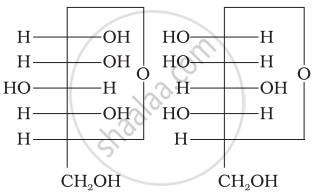
Three structures are given below in which two glucose units are linked. Which of these linkages between glucose units are between C1 and C4 and which linkages are between C1 and C6?
| (I) |  |
| (II) | 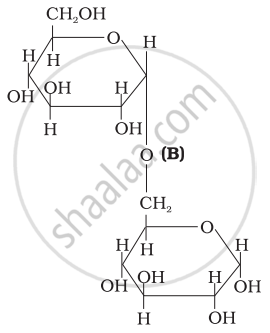 |
| (III) | 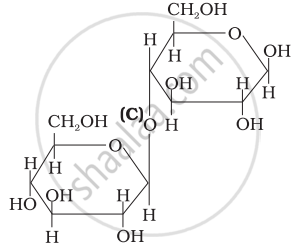 |
(A) is between C1 and C4, (B) and (C) are between C1 and C6
(A) and (B) are between C1 and C4, (C) is between C1 and C6
(A) and (C) are between C1 and C4, (B) is between C1 and C6
(A) and (C) are between C1 and C6, (B) is between C1 and C4
Carbohydrates are classified on the basis of their behaviour on hydrolysis and also as reducing or non-reducing sugar. Sucrose is a:
(i) monosaccharide
(ii) disaccharide
(iii) reducing sugar
(iv) non-reducing sugar
Proteins can be classified into two types on the basis of their molecular shape i.e., fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins are:
(i) Insulin
(ii) Keratin
(iii) Albumin
(iv) Myosin
Which of the following carbohydrates are branched polymers of glucose?
(i) Amylose
(ii) Amylopectin
(iii) Cellulose
(iv) Glycogen
Amino acids are classified as acidic, basic or neutral depending upon the relative number of amino and carboxyl groups in their molecule. Which of the following are acidic?
(i)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{(CH3)2CH - CH - COOH}\\
\phantom{..}|\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{NH2}
\end{array}\]
(ii)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{HOOC - CH2 - CH2 - CH - COOH}\\
\phantom{............}|\\
\phantom{...............}\ce{NH2}
\end{array}\]
(iii)
\[\ce{H2N - CH2 - CH2 - CH2 - COOH}\]
(iv)
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{HOOC - CH2 - CH - COOH}\\
\phantom{.....}|\\
\phantom{........}\ce{NH2}
\end{array}\]
Lysine, \[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H2N - (CH2)4 - CH - COOH}\\
\phantom{.....}|\\
\phantom{........}\ce{NH2}
\end{array}\] is:
(i) α-Amino acid
(ii) Basic amino acid
(iii) Amino acid synthesised in body
(iv) β-Amino acid
Which of the following monosaccharides are present as five membered cyclic structure (furanose structure)?
(i) Ribose
(ii) Glucose
(iii) Fructose
(iv) Galactose
In fibrous proteins, polypeptide chains are held together by:
(i) van der Waals forces
(ii) disulphide linkage
(iii) electrostatic forces of attraction
(iv) hydrogen bonds
Which of the following are purine bases?
(i) Guanine
(ii) Adenine
(iii) Thymine
(iv) Uracil
Which of the following terms are correct about enzyme?
(i) Proteins
(ii) Dinucleotides
(iii) Nucleic acids
(iv) Biocatalysts
Name the sugar present in milk. How many monosaccharide units are present in it? What are such oligosaccharides called?
How do you explain the presence of all the six carbon atoms in glucose in a straight chain?
In nucleoside a base is attached at 1′ position of sugar moiety. Nucleotide is formed by linking of phosphoric acid unit to the sugar unit of nucleoside. At which position of sugar unit is the phosphoric acid linked in a nucleoside to give a nucleotide?
Name the linkage connecting monosaccharide units in polysaccharides.
Under what conditions glucose is converted to gluconic and saccharic acid?
Monosaccharides contain carbonyl group hence are classified, as aldose or ketose. The number of carbon atoms present in the monosaccharide molecule are also considered for classification. In which class of monosaccharide will you place fructose?
The letters ‘D’ or ‘L’ before the name of a stereoisomer of a compound indicate the correlation of configuration of that particular stereoisomer. This refers to their relation with one of the isomers of glyceraldehyde. Predict whether the following compound has ‘D’ or ‘L’ configuration.
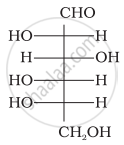
Aldopentoses named as ribose and 2-deoxyribose are found in nucleic acids. What is their relative configuration?
Which type of biomolecules have some structural similarity with synthetic polyamides? What is this similarity?
Which sugar is called invert sugar? Why is it called so?
Amino acids can be classified as α–, β–, γ–, δ– and so on depending upon the relative position of amino group with respect to carboxyl group. Which type of amino acids form polypetide chain in proteins?
α-Helix is a secondary structure of proteins formed by twisting of polypeptide chain into right-handed screw like structures. Which type of interactions are responsible for making the α-helix structure stable?
Some enzymes are named after the reaction, where they are used. What name is given to the class of enzymes which catalyse the oxidation of one substrate with simultaneous reduction of another substrate.
During curdling of milk, what happens to sugar present in it?
How do you explain the presence of five – OH groups in glucose molecule?
Why does compound (A) given below not form an oxime?
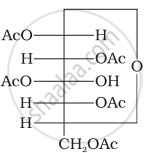
(A)
Why must vitamin C be supplied regularly in diet?
Sucrose is dextrorotatory but the mixture obtained after hydrolysis is laevorotatory. Explain.
Amino acids behave like salts rather than simple amines or carboxylic acids. Explain.
Structures of glycine and alanine are given below. Show the peptide linkage in glycylalanine.
\[\ce{\underset{(Glycine)}{H2N - CH2 - COOH}}\];
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H2N - CH2 - COOH}\\
|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{\underset{(Alanine)}{CH3}\phantom{...}}
\end{array}\]
Protein found in a biological system with a unique three-dimensional structure and biological activity is called a native protein. When a protein in its native form, is subjected to a physical change like change in temperature or a chemical change like, change in pH, denaturation of protein takes place. Explain the cause.
Activation energy for the acid catalysed hydrolysis of sucrose is 6.22 kJ mol–1, while the activation energy is only 2.15 kJ mol–1 when hydrolysis is catalysed by the enzyme sucrase. Explain.
How do you explain the presence of an aldehydic group in a glucose molecule?
Which moieties of nucleosides are involved in the formation of phosphodiester linkages present in dinucleotides? What does the word diester in the name of linkage indicate? Which acid is involved in the formation of this linkage?
What are glycosidic linkages? In which type of biomolecules are they present?
Which monosaccharide units are present in starch, cellulose and glucose and which linkages link these units?
How do enzymes help a substrate to be attacked by the reagent effectively?
Describe the term D- and L- configuration used for amino acids with examples.
How will you distinguish 1° and 2° hydroxyl groups present in glucose? Explain with reactions.
Coagulation of egg white on boiling is an example of denaturation of protein. Explain it in terms of structural changes.
Match the vitamins given in Column I with the deficiency disease they cause given in Column II.
| Column I (Vitamins) | Column II (Diseases) |
| (i) Vitamin A | (a) Pernicious anaemia |
| (ii) Vitamin B1 | (b) Increased blood clotting time |
| (iii) Vitamin B12 | (c) Xerophthalmia |
| (iv) Vitamin C | (d) Rickets |
| (v) Vitamin D | (e) Muscular weakness |
| (vi) Vitamin E | (f) Night blindness |
| (vii) Vitamin K | (g) Beri Beri |
| (h) Bleeding gums | |
| (i) Osteomalacia |
Match the following enzyms given in Column I with the reactions they catalyse given in Column II.
| Column I (Enzymes) | Column II (Reactions) |
| (i) Invertase | (a) Decomposition of urea into NH3 and CO2 |
| (ii) Maltase | (b) Conversion of glucose into ethyl alcohol |
| (iii) Pepsin | (c) Hydrolysis of maltose into glucose |
| (iv) Urease | (d) Hydrolysis of cane sugar |
| (v) Zymase | (e) Hydrolysis of proteins into peptides |
Assertion: D (+) – Glucose is dextrorotatory in nature.
Reason: ‘D’ represents its dextrorotatory nature.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion: Vitamin D can be stored in our body.
Reason: Vitamin D is fat-soluble vitamin.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion: β-glycosidic linkage is present in maltose,

Reason: Maltose is composed of two glucose units in which C–1 of one glucose unit is linked to C–4 of another glucose unit.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion: All naturally occurring α-aminoacids except glycine are optically active.
Reason: Most naturally occurring amino acids have L-configuration.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion: Deoxyribose, \[\ce{C5H10O4}\] is not a carbohydrate.
Reason: Carbohydrates are hydrates of carbon so compounds which follow \[\ce{C_x(H2O)_y}\] formula are carbohydrates.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion: Glycine must be taken through diet.
Reason: It is an essential amino acid.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain assertion.
Assertion: In presence of enzyme, substrate molecule can be attacked by the reagent effectively.
Reason: Active sites of enzymes hold the substrate molecule in a suitable position.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements and reason explains the assertion.
Both assertion and reason are wrong statements.
Assertion is correct statement and reason is wrong statement.
Assertion is wrong statement and reason is correct statement.
Assertion and reason both are correct statements but reason does not explain assertion.
Write the reactions of D-glucose which can’t be explained by its open-chain structure. How can cyclic structure of glucose explain these reactions?
On the basis of which evidences D-glucose was assigned the following structure?
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CHO}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\phantom{..}\ce{(CHOH)4}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\phantom{..}\ce{CH2OH}
\end{array}\]
Carbohydrates are essential for life in both plants and animals. Name the carbohydrates that are used as storage molecules in plants and animals, also name the carbohydrate which is present in wood or in the fibre of cotton cloth.
Explain the terms primary and secondary structure of proteins. What is the difference between α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure of proteins?
Write the structures of fragments produced on complete hydrolysis of DNA. How are they linked in DNA molecule? Draw a diagram to show pairing of nucleotide bases in double helix of DNA.
Solutions for 14: Biomolecules
![NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 14 - Biomolecules NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 14 - Biomolecules - Shaalaa.com](/images/chemistry-english-class-12_6:5f2b1b2038084cf381bfa42c826a928c.jpg)
NCERT Exemplar solutions for Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 14 - Biomolecules
Shaalaa.com has the CBSE Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE solutions in a manner that help students grasp basic concepts better and faster. The detailed, step-by-step solutions will help you understand the concepts better and clarify any confusion. NCERT Exemplar solutions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE 14 (Biomolecules) include all questions with answers and detailed explanations. This will clear students' doubts about questions and improve their application skills while preparing for board exams.
Further, we at Shaalaa.com provide such solutions so students can prepare for written exams. NCERT Exemplar textbook solutions can be a core help for self-study and provide excellent self-help guidance for students.
Concepts covered in Chemistry [English] Class 12 chapter 14 Biomolecules are Introduction of Carbohydrates, Classification of Carbohydrates, Monosaccahrides, Importance of Carbohydrates, Introduction of Proteins, Amino Acids, Structure of Proteins, Introduction of Vitamins, Introduction of Nucleic Acids, Preparation of Glucose, Structures of Glucose, Disaccharides - Sucrose, Maltose and Lactose, Polysaccharides - Starch, Cellulose and Glycogen, Classification of Amino Acids, Introduction of Enzymes, Mechanism of Enzyme Action, Denaturation of Proteins, Structure of Fructose, Classification of Vitamins, Chemical Composition of Nucleic Acids, Structure of Nucleic Acids, Biological Functions of Nucleic Acids, Biomolecules Numericals, Peptide, Oligosaccharides, Polysaccharides, Chemical Coordination, Lipids and Hormones.
Using NCERT Exemplar Chemistry [English] Class 12 solutions Biomolecules exercise by students is an easy way to prepare for the exams, as they involve solutions arranged chapter-wise and also page-wise. The questions involved in NCERT Exemplar Solutions are essential questions that can be asked in the final exam. Maximum CBSE Chemistry [English] Class 12 students prefer NCERT Exemplar Textbook Solutions to score more in exams.
Get the free view of Chapter 14, Biomolecules Chemistry [English] Class 12 additional questions for Mathematics Chemistry [English] Class 12 CBSE, and you can use Shaalaa.com to keep it handy for your exam preparation.