Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Three structures are given below in which two glucose units are linked. Which of these linkages between glucose units are between C1 and C4 and which linkages are between C1 and C6?
| (I) |  |
| (II) | 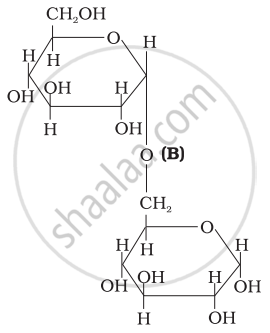 |
| (III) | 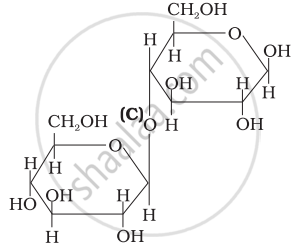 |
Options
(A) is between C1 and C4, (B) and (C) are between C1 and C6
(A) and (B) are between C1 and C4, (C) is between C1 and C6
(A) and (C) are between C1 and C4, (B) is between C1 and C6
(A) and (C) are between C1 and C6, (B) is between C1 and C4
Solution
(A) and (C) are between C1 and C4, (B) is between C1 and C6
Explanation:
(A) and (C) are between Cl and C4, (B) is between Cl and C6.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Enumerate the reactions of D-glucose which cannot be explained by its open chain structure.
Glucose on reaction with HI gives n-hexane. What does it suggest about the structure of glucose?
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets:
(iodoform, acetaldehyde, positive, greater, acidic, acetone, disaccharide, negative, increases, glucose, decreases, chloroform, polysaccharide, lactose, lesser, basic, cationic hydrolysis, anionic hydrolysis)
Sucrose is a _________ and yields upon hydrolysis, a mixture of ________ and fructose.
Write the reactions involved when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent:
(CH3CO)2O
The spatial arrangement of the given molecule is denoted by:

Which one of the following compounds is different from the rest?
When glucose reacts with bromine water, the main product is ____________.
The letter D and L in carbohydrates represent ____________.
Write the reactions of D-glucose which can’t be explained by its open-chain structure. How can cyclic structure of glucose explain these reactions?
Give a reason for the following observations:
Penta-acetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine.
