Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Enumerate the reactions of D-glucose which cannot be explained by its open chain structure.
Solution 1
(1) Aldehydes give 2, 4-DNP test, Schiff’s test, and react with NaHSO4 to form the hydrogen sulphite addition product. However, glucose does not undergo these reactions.
(2) The pentaacetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine. This indicates that a free −CHO group is absent from glucose.
(3) Glucose exists in two crystalline forms − ∝ andβ. The ∝-form (m.p. = 419 K) crystallises from a concentrated solution of glucose at 303 K and the β-form (m.p = 423 K) crystallises from a hot and saturated aqueous solution at 371 K. This behaviour cannot be explained by the open chain structure of glucose.
Solution 2
D (+) – glucose does not undergo certain characteristic reactions of aldehydes, e.g., glucose does not form NaHSO3 addition product.
Glucose reacts with NH2OH to form an oxime but glucose pentaacetate does not. This implies that the aldehydic group is absent in glucose pentaacetate.
D – (+) – glucose exists in two stereoisomeric forms, i.e., α -glucose and β-glucose.
Both α – D – glucose and β – D – glucose undergo mutarotation in aqueous solution. Although the crystalline forms of α- and β -D (+) – glucose are quite stable in aqueous solution but each form slowly changes into an equilibrium mixture of both.
D (+) – glucose forms two isomeric methyl glucosides. Aldehydes normally react with two moles of methanol per mole of the aldehyde to form an acetal but D (+) – glucose when treated with methanol in presence of dry HCl gas, reacts with only one mole of methanol per mole of glucose to form a mixture of two methyl D – glucosides i. e., methyl – α – D – glucoside (melting point 43 8 K, specific rotation +158°) and methyl – β – D – glucoside (melting point 308 K, specific rotation – 33°).
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw the simple Fisher projection formulae of D - (+) - glucose and D - (-) - fructose
How many moles of acetic anhydride will be required to form glucose pentaacetate from 2M of glucose?
(a) 2
(b) 5
(c) 10
(d) 2.5
Glucose on reaction with HI gives n-hexane. What does it suggest about the structure of glucose?
Differentiable between the following:
Amylose and Amylopectin
Write the reactions involved when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent:
Br2 water
The following compound can be called as:
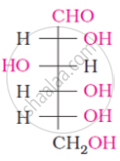
The spatial arrangement of the given molecule is denoted by:

When glucose reacts with bromine water, the main product is ____________.
The α-D glucose and β-D glucose differ from each other due to difference in carbon atom with respect to its ____________.
Choose the correct relationship for glucose and fructose:
The letter D and L in carbohydrates represent ____________.
Which of the following pairs represents anomers?
Why does compound (A) given below not form an oxime?
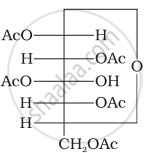
(A)
Assertion: D (+) – Glucose is dextrorotatory in nature.
Reason: ‘D’ represents its dextrorotatory nature.
Write the reactions of D-glucose which can’t be explained by its open-chain structure. How can cyclic structure of glucose explain these reactions?
Match List - I with List - II.
| List I | List II | ||
| (A) | Glucose + HI | (I) | Gluconic acid |
| (B) | Glucose + Br2 water | (II) | Glucose pentacetate |
| (C) | Glucose + acetic anhydride | (III) | Saccharic acid |
| (D) | Glucose + HNO3 | (IV) | Hexane |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
When D-glucose reacts with HI, it forms ______.
Give a reason for the following observations:
Penta-acetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine.
