Advertisements
Advertisements
Questions
Write the reactions involved when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent:
Br2 water
What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent?
Bromine water
Solution
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{........}\ce{CHO}\phantom{.............}\ce{COOH}\phantom{..}\\
\phantom{.}|\phantom{..................}|\\
\phantom{.......}\ce{(CHOH)4->[Br2 water](CHOH)4}\\
\phantom{.}|\phantom{..................}|\\
\phantom{............}\ce{\underset{\text{D-glucose}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{.........}\ce{\underset{\text{D-gluconic acid}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{.}
\end{array}\]
RELATED QUESTIONS
How many moles of acetic anhydride will be required to form glucose pentaacetate from 2M of glucose?
(a) 2
(b) 5
(c) 10
(d) 2.5
What happens when glucose is treated with hydroxylamine?
Maltose is a
(a) Polysaccharide
(b) Disaccharide
(c) Trisaccharide
(d) Monosaccharide
Enlist the properties of glucose that can not be explained on the basis of open chain structure of it
What happens when glucose is treated with hydrogen cyanide?
Answer the following question.
What is the basic structural difference between glucose and fructose?
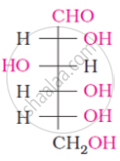
The following compound can be called as:
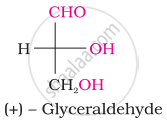
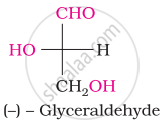
Choose the appropriate answer(s) for the below representation from the options given
Glucose does not react with ____________.
Which of the following reactions of glucose can be explained only by its cyclic structure?
Which is the least stable form of glucose?
The number of chiral carbon atoms present in cyclic structure α-D(+) glucose:
Which one is correct?
In the following reaction, identify A and B:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{C6H12O6 ->[Acetic anhydride] A}\\
\downarrow \text{Conc. nitric acid}\phantom{...}\\
\ce{B}\phantom{.................}\end{array}\]
Assertion: D (+) – Glucose is dextrorotatory in nature.
Reason: ‘D’ represents its dextrorotatory nature.
What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent?
HI
Account for the following:
There are 5 OH groups in glucose
Account for the following:
What happens when D – glucose is treated with the following reagents
HNO3
The number of asymmetric carbon atoms in the glucose molecule in open and cyclic form is ______.
