Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Account for the following:
What happens when D – glucose is treated with the following reagents
HNO3
Solution
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\phantom{......}\ce{CHO}\phantom{.............}\ce{COOH}\phantom{.............}\ce{COOH}\phantom{......}\\
\phantom{...}|\phantom{..................}|\phantom{...................}|\phantom{........}\\
\phantom{.}\ce{(CHOH)4 ->[Oxidation] (CHOH)4 <-[Oxidation] (CHOH)4}\\
\phantom{...}|\phantom{..................}|\phantom{...................}|\phantom{........}\\
\phantom{.....}\ce{CH2OH}\phantom{...........}\ce{\underset{\underset{acid}{Saccharic}}{COOH}}\phantom{.............}\ce{\underset{\underset{acid}{Gluconic}}{CH2OH}}\phantom{....}
\end{array}\]
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Write the reaction that indicates the presence of -CHO group in glucose
Glucose on reaction with HI gives n-hexane. What does it suggest about the structure of glucose?
Answer the following question.
What is the basic structural difference between glucose and fructose?
Write the reactions involved when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent:
H2N-OH
Choose the appropriate answer(s) for the below representation from the options given
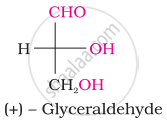
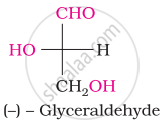
The number of asymmetric carbon atom(s) below the figure is/are

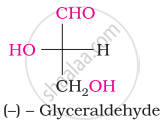
Which is the least stable form of glucose?
The two forms of D-glucopyranose obtained from the solution of D-glucose are called ____________.
Three structures are given below in which two glucose units are linked. Which of these linkages between glucose units are between C1 and C4 and which linkages are between C1 and C6?
| (I) |  |
| (II) | 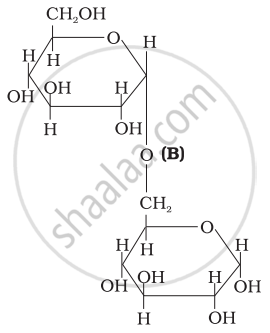 |
| (III) | 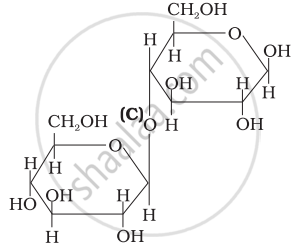 |
Match List - I with List - II.
| List I | List II | ||
| (A) | Glucose + HI | (I) | Gluconic acid |
| (B) | Glucose + Br2 water | (II) | Glucose pentacetate |
| (C) | Glucose + acetic anhydride | (III) | Saccharic acid |
| (D) | Glucose + HNO3 | (IV) | Hexane |
Choose the correct answer from the options given below:
