Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Maltose is a
(a) Polysaccharide
(b) Disaccharide
(c) Trisaccharide
(d) Monosaccharide
Solution
Disaccharide
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw the simple Fisher projection formulae of D - (+) - glucose and D - (-) - fructose
What happens when glucose is treated with hydrogen cyanide?
Glucose on reaction with HI gives n-hexane. What does it suggest about the structure of glucose?
Differentiable between the following:
Amylose and Amylopectin
What do you observe when glucose solution is heated with Tollen’s reagent?
Fill in the blanks by choosing the appropriate word/words from those given in the brackets:
(iodoform, acetaldehyde, positive, greater, acidic, acetone, disaccharide, negative, increases, glucose, decreases, chloroform, polysaccharide, lactose, lesser, basic, cationic hydrolysis, anionic hydrolysis)
Sucrose is a _________ and yields upon hydrolysis, a mixture of ________ and fructose.
What do you observe when glucose is treated with bromine water?
Write the reactions involved when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent:
H2N-OH
The following compound can be called as:
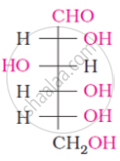
The spatial arrangement of the given molecule is denoted by:

Choose the appropriate answer(s) for the below representation from the options given
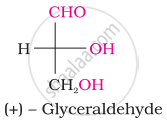
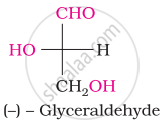
The number of asymmetric carbon atom(s) below the figure is/are

What is the most abundant organic compound on earth?
Oxime is formed by treating glucose with ____________.
The symbols D and L represents ____________.
Which one of the following compounds is different from the rest?
When glucose reacts with bromine water, the main product is ____________.
A solution of D-glucose in water rotates the plane polarised light ____________.
Which one is correct?
Which one of the following reactions is not explained by the open chain Structure of glucose?
In the following reaction, identify A and B:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{C6H12O6 ->[Acetic anhydride] A}\\
\downarrow \text{Conc. nitric acid}\phantom{...}\\
\ce{B}\phantom{.................}\end{array}\]
Which of the following pairs represents anomers?
Three structures are given below in which two glucose units are linked. Which of these linkages between glucose units are between C1 and C4 and which linkages are between C1 and C6?
| (I) |  |
| (II) | 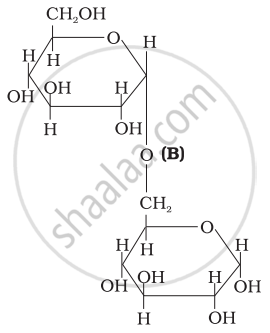 |
| (III) | 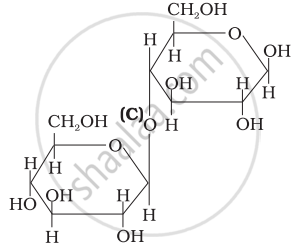 |
Why does compound (A) given below not form an oxime?
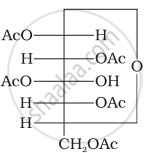
(A)
Write the reactions of D-glucose which can’t be explained by its open-chain structure. How can cyclic structure of glucose explain these reactions?
Account for the following:
What happens when D – glucose is treated with the following reagents
HNO3
Consider the following reactions:
(i) \[\ce{Glucose + R-OH ->[Conc. HNO3] [A] ->[X eq of][(CH3CO)2O] Acetyl derivative}\]
(ii) \[\ce{Glucose ->[Ni/H2] [A] ->[Y eq of][(CH3CO)2O] Acetyl derivative}\]
(iii) \[\ce{Glucose ->[Z eq of][(CH3CO)2O] Acetyl derivative}\]
'X, 'Y' and 'Z' in these reactions are respectively:
When D-glucose reacts with HI, it forms ______.
Give the reaction of glucose with hydrogen cyanide. Presence of which group is confirmed by this reaction?
