Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Enlist the properties of glucose that can not be explained on the basis of open chain structure of it
Solution
Although the open chain structure of D (+) − Glucose explains most of its reactions, it fails to explain the following facts:
a) D (+)-Glucose does not undergo certain characteristic reactions of aldehydes
eg., Glucose does not form NaHSO3 addition product, aldehyde-ammonia adduct 2, 4 − DNP derivative and does not respond to Schiff’s reagent test.
b) Glucose reacts with NH2OH to form an oxime but glucose pentaacetate does not react
with NH2OH, which implies that the free aldehyde group is absent in glucose pentaacetate
c) D(+)-Glucose exists in two stereoisomeric crystalline forms, i.e. α-glucose and
β-glucose, called anomers. α-D(+)-Glucose is obtained when a concentrated aqueous or
alcoholic solution is crystallised at 303 K. It has a melting point of 419 K and has a
specific rotation of +111° in a freshly prepared aqueous solution.
However, when glucose is crystallised from water above 371 K, β-D(+)-glucose is
obtained. It has a melting point of 423 K and has a specific rotation of +19.2° in a
freshly prepared aqueous solution. This behaviour could not be explained by the open
chain structure of glucose.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Draw the simple Fisher projection formulae of D - (+) - glucose and D - (-) - fructose
What happens when glucose is treated with hydroxylamine?
Maltose is a
(a) Polysaccharide
(b) Disaccharide
(c) Trisaccharide
(d) Monosaccharide
What happens when glucose is treated with hydrogen cyanide?
Glucose on reaction with HI gives n-hexane. What does it suggest about the structure of glucose?
What do you observe when glucose solution is heated with Tollen’s reagent?
Write the reactions involved when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent:
Br2 water
Write the reactions involved when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent:
H2N-OH
What is the most abundant organic compound on earth?
When glucose reacts with bromine water, the main product is ____________.
Glucose is found to exist in two different α and β crystalline forms. These forms can be obtained by:
(i) The α form of glucose is obtained by crystallisation from a concentrated solution of glucose at 303 K.
(ii) The β form of glucose is obtained by crystallisation from a concentrated solution of glucose at 303 K.
(iii) The β form is obtained by crystallisation from hot and saturated aqueous solution at 371 K.
(iv) The α form is obtained by crystallisation from hot and saturated aqueous solution at 371 K.
Reduction of glucose by HI suggest that ____________.
The reaction of glucose with red P + HI is called ____________.
The α-D glucose and β-D glucose differ from each other due to difference in carbon atom with respect to its ____________.
The two forms of D-glucopyranose obtained from the solution of D-glucose are called ____________.
In the following reaction, identify A and B:
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{C6H12O6 ->[Acetic anhydride] A}\\
\downarrow \text{Conc. nitric acid}\phantom{...}\\
\ce{B}\phantom{.................}\end{array}\]
Three structures are given below in which two glucose units are linked. Which of these linkages between glucose units are between C1 and C4 and which linkages are between C1 and C6?
| (I) |  |
| (II) | 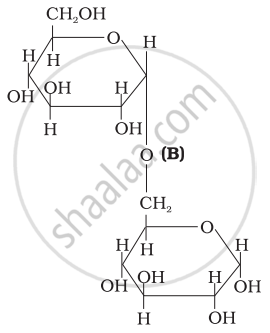 |
| (III) | 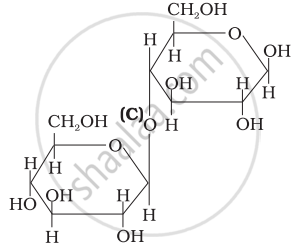 |
Assertion: D (+) – Glucose is dextrorotatory in nature.
Reason: ‘D’ represents its dextrorotatory nature.
On the basis of which evidences D-glucose was assigned the following structure?
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{CHO}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\phantom{..}\ce{(CHOH)4}\\
|\phantom{....}\\
\phantom{..}\ce{CH2OH}
\end{array}\]
What happens when D-glucose is treated with the following reagent?
HI
Account for the following:
There are 5 OH groups in glucose
Account for the following:
What happens when D – glucose is treated with the following reagents
Bromine water
Glucose with excess of phenyl hydrazine forms ______.
When D-glucose reacts with HI, it forms ______.
Give a reason for the following observations:
Penta-acetate of glucose does not react with hydroxylamine.
