Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
| (I) | 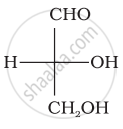 |
| (II) | 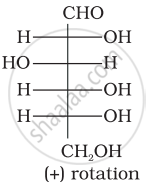 |
| (III) | 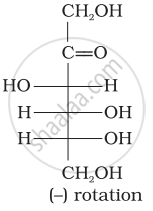 |
Options
I, II, III
II, III
I, II
III
Solution
I, II, III
Explanation:
I, II and III structures have D configuration with –OH group on the lowest asymmetric carbon is on the right side which is comparable to (+) glyceraldehyde.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
What are the common types of secondary structure of proteins?
The helical structure of protein is stabilized by:
The correct statement for protein haemoglobin.
Which of the following statement is correct:
α-Helix is a secondary structure of proteins formed by twisting of polypeptide chain into right-handed screw like structures. Which type of interactions are responsible for making the α-helix structure stable?
Structures of glycine and alanine are given below. Show the peptide linkage in glycylalanine.
\[\ce{\underset{(Glycine)}{H2N - CH2 - COOH}}\];
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H2N - CH2 - COOH}\\
|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{\underset{(Alanine)}{CH3}\phantom{...}}
\end{array}\]
Protein found in a biological system with a unique three-dimensional structure and biological activity is called a native protein. When a protein in its native form, is subjected to a physical change like change in temperature or a chemical change like, change in pH, denaturation of protein takes place. Explain the cause.
Which moieties of nucleosides are involved in the formation of phosphodiester linkages present in dinucleotides? What does the word diester in the name of linkage indicate? Which acid is involved in the formation of this linkage?
Each polypeptide in a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is said to be ______.
Proteins are polymers of ______.
