Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Structures of glycine and alanine are given below. Show the peptide linkage in glycylalanine.
\[\ce{\underset{(Glycine)}{H2N - CH2 - COOH}}\];
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H2N - CH2 - COOH}\\
|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{\underset{(Alanine)}{CH3}\phantom{...}}
\end{array}\]
Solution
In glycylalanine, carboxyl group of glycine combines with the amino group of alanine.

APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Discuss the optical activity of lactic acid.
What are the common types of secondary structure of proteins?
Write one difference between α-helix and β-pleated structures of proteins.
The protein responsible for blood clotting is ____________.
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
| (I) | 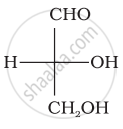 |
| (II) | 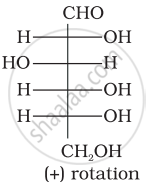 |
| (III) | 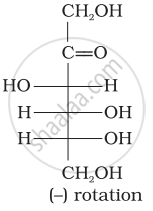 |
Proteins can be classified into two types on the basis of their molecular shape i.e., fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins are:
(i) Insulin
(ii) Keratin
(iii) Albumin
(iv) Myosin
Presence of disulphide link gives rise to which structure of protein?
The correct structure of Ruhemann's Purple, the compound formed in the reaction of ninhydrin with proteins is:
Assertion (A): Proteins are polymers of α-amino acids connected by a peptide bond.
Reason (R): A tetrapeptide contains 4 amino acids linked by 4 peptide bonds.
What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
