Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Discuss the optical activity of lactic acid.
Solution
(1) Lactic acid contains one asymmetric carbon atom which is attached to four different groups, COOH, CH3, OH and H.
(2) Two different arrangements of these groups around the carbon atom are possible as shown in the figure. Hence, it exist as a pair of enantiomers. The two enantiomers are mirror images of each other and are non-superimposable.
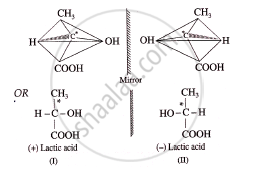
(3) Hence, lactic acid can exist in two different forms, d-Form and l-form, which are non-superimposable mirror images of each other. d-form rotates the plane of plane-polarized light to the right, while l-form rotates the same to the left.
(4) A mixture containing equimolar amounts of the d- and l-forms is a racemic mixture which is optically inactive (dl - form). This inactivity arises due to external compensation.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are proteins classified on the basis of molecular shapes?
What is peptide linkage?
Differentiate between the following :
Fibrous proteins and Globular proteins
Differentiate between the following :
Peptide linkage and Glycosidic linkage
The protein responsible for blood clotting is ____________.
The correct statement for protein haemoglobin.
Which functional group participates in disulphide bond formation in proteins?
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
| (I) | 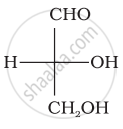 |
| (II) | 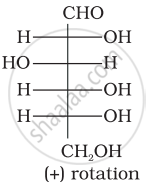 |
| (III) | 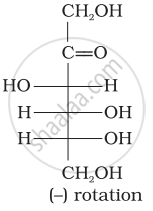 |
Proteins can be classified into two types on the basis of their molecular shape i.e., fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins are:
(i) Insulin
(ii) Keratin
(iii) Albumin
(iv) Myosin
α-Helix is a secondary structure of proteins formed by twisting of polypeptide chain into right-handed screw like structures. Which type of interactions are responsible for making the α-helix structure stable?
Which moieties of nucleosides are involved in the formation of phosphodiester linkages present in dinucleotides? What does the word diester in the name of linkage indicate? Which acid is involved in the formation of this linkage?
Assertion: β-glycosidic linkage is present in maltose,

Reason: Maltose is composed of two glucose units in which C–1 of one glucose unit is linked to C–4 of another glucose unit.
Explain the terms primary and secondary structure of proteins. What is the difference between α-helix and β-pleated sheet structure of proteins?
Each polypeptide in a protein has amino acids linked with each other in a specific sequence. This sequence of amino acids is said to be ______.
Peptide linkage is:
Explain formation of peptide linkage in protein with an example.
Presence of disulphide link gives rise to which structure of protein?
The correct structure of Ruhemann's Purple, the compound formed in the reaction of ninhydrin with proteins is:
The total number of negative charge in the tetrapeptide, Gly-Glu-Asp-Tyr at pH 12.5 will be ______. (Integer answers)
Proteins are polymers of ______.
Assertion (A): Proteins are polymers of α-amino acids connected by a peptide bond.
Reason (R): A tetrapeptide contains 4 amino acids linked by 4 peptide bonds.
What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
Write a classification of proteins with an example.
