Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
Presence of disulphide link gives rise to which structure of protein?
Solution
Tertiary structure of protein
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
How are proteins classified on the basis of molecular shapes?
What is peptide linkage?
Discuss the optical activity of lactic acid.
What type of bonding helps in stabilising the ∝-helix structure of proteins?
Differentiate between the following :
Fibrous proteins and Globular proteins
Write one difference between α-helix and β-pleated structures of proteins.
Differentiate between the following :
Peptide linkage and Glycosidic linkage
Which of the following biomolecules is insoluble in water?
The protein responsible for blood clotting is ____________.
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
| (I) | 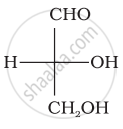 |
| (II) | 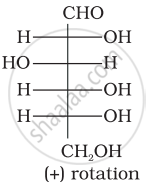 |
| (III) | 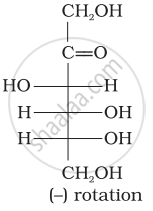 |
Proteins can be classified into two types on the basis of their molecular shape i.e., fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins are:
(i) Insulin
(ii) Keratin
(iii) Albumin
(iv) Myosin
Which of the following are purine bases?
(i) Guanine
(ii) Adenine
(iii) Thymine
(iv) Uracil
α-Helix is a secondary structure of proteins formed by twisting of polypeptide chain into right-handed screw like structures. Which type of interactions are responsible for making the α-helix structure stable?
The main structural feature of proteins is
Peptide linkage is:
Explain formation of peptide linkage in protein with an example.
The total number of negative charge in the tetrapeptide, Gly-Glu-Asp-Tyr at pH 12.5 will be ______. (Integer answers)
An α-helix is a structural feature of ______.
β-pleated sheet structure in proteins refers to ______.
What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
Write a classification of proteins with an example.
