Advertisements
Advertisements
Question
What type of bonding helps in stabilising the α-helix structure of proteins?
Solution
α-Helix is one of the most common ways in which a polypeptide chain forms all possible hydrogen bonds by twisting into a right handed screw (helix) with the –NH group of each amino acid residue hydrogen bonded to the \[\begin{array}{cc}\backslash\phantom{.....}\\\ce{C=O}\\/\phantom{......}\end{array}\] of an adjacent turn of the helix.
APPEARS IN
RELATED QUESTIONS
Discuss the optical activity of lactic acid.
Define the following as related to proteins:
Peptide linkage
Differentiate between the following :
Peptide linkage and Glycosidic linkage
The correct statement for protein haemoglobin.
Which functional group participates in disulphide bond formation in proteins?
Which of the following statement is correct:
Optical rotations of some compounds along with their structures are given below which of them have D configuration.
| (I) | 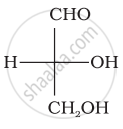 |
| (II) | 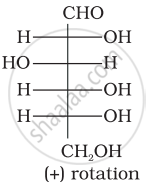 |
| (III) | 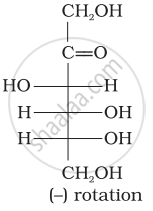 |
Proteins can be classified into two types on the basis of their molecular shape i.e., fibrous proteins and globular proteins. Examples of globular proteins are:
(i) Insulin
(ii) Keratin
(iii) Albumin
(iv) Myosin
In fibrous proteins, polypeptide chains are held together by:
(i) van der Waals forces
(ii) disulphide linkage
(iii) electrostatic forces of attraction
(iv) hydrogen bonds
α-Helix is a secondary structure of proteins formed by twisting of polypeptide chain into right-handed screw like structures. Which type of interactions are responsible for making the α-helix structure stable?
Structures of glycine and alanine are given below. Show the peptide linkage in glycylalanine.
\[\ce{\underset{(Glycine)}{H2N - CH2 - COOH}}\];
\[\begin{array}{cc}
\ce{H2N - CH2 - COOH}\\
|\phantom{......}\\
\ce{\underset{(Alanine)}{CH3}\phantom{...}}
\end{array}\]
Assertion: β-glycosidic linkage is present in maltose,

Reason: Maltose is composed of two glucose units in which C–1 of one glucose unit is linked to C–4 of another glucose unit.
Given below are two statements labelled as Assertion (A) and Reason (R).
Assertion (A): Proteins are found to have two different types of secondary structures viz alpha-helix and beta-pleated sheet structure.
Reason (R): The secondary structure of proteins is stabilized by hydrogen bonding.
Select the most appropriate answer from the options given below:
Presence of disulphide link gives rise to which structure of protein?
Out of the following, which type of interaction is responsible for the stabilisation of the α-helix structure of proteins?
The correct structure of Ruhemann's Purple, the compound formed in the reaction of ninhydrin with proteins is:
The total number of negative charge in the tetrapeptide, Gly-Glu-Asp-Tyr at pH 12.5 will be ______. (Integer answers)
Proteins are polymers of ______.
What is the effect of denaturation on the structure of proteins?
